Stryd Running Power review
Stryd is one of the most useful and impressive running technologies available, with four key benefits.
- Accurate Pace. Stryd is a Footpod with vastly greater accuracy than GPS, providing much better pace and distance data. It's accurate enough that it really doesn't need any calibration, and unlike GPS, it should work in any situation (see below for details.) Because of it's accuracy, it can provide real-time pace, something that's impractical to achieve with any GPS device as GPS requires quite a bit of smoothing, giving only a recent average pace.
- Running Power. While a Running Power Meters are quite different to cycling power meters and are more of a "power estimate" than a true meter, Stryd's power estimate has improved to the point where it's a valuable training and racing tool. Unless you run on perfectly flat ground, running power is a better measure of effort than pace.
- Fitness Measure. I use the relationship between Stryd's power and my heart rate to evaluate my fitness over time, as well as my fatigue during a run. This HrPwr has been more useful to me than any other metric as it can be calculated in real time.
- Running Form. Stryd is the first device I've found that provides data on your running form that is actionable. While other devices can provide a lot more data, it's typically hard to work out what the data means. Stryd allows you to compare your running form with other runners, which can show areas for improvement. Both the Footpath Visualization and the Stryder Distribution can give meaningful and usable insight into your running form. Hopefully, Stryd will continue to improve this data, allowing you to compare your footpath and distribution with runners based on their fitness (crucial power.)
At $220 I think that Stryd is good value for money, and it's one of the few running devices that I would replace unhesitatingly if I lost it.

| This review was made possible by readers like you buying products via my links. I buy all the products I review through normal retail channels, which allows me to create unbiased reviews free from the influence of reciprocity, or the need to keep vendors happy. It also ensures I don't get "reviewer specials" that are better than the retail versions.
|
Contents
1 The Metrics
Stryd provides an array of different metrics, which vary both in accuracy and usefulness.
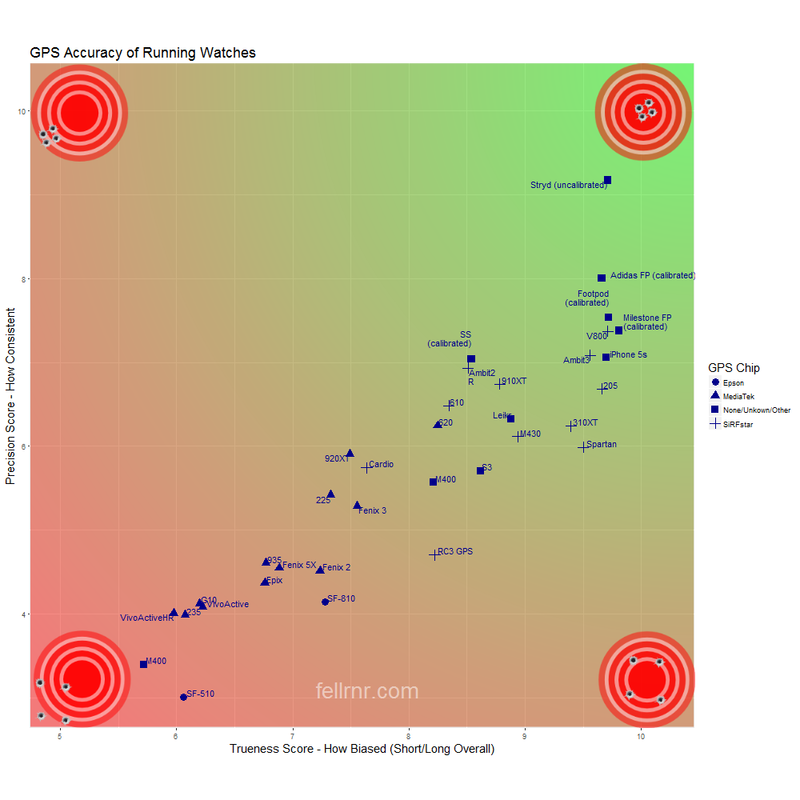
- Pace and Distance. My testing has shown that the Stryd is stunningly accurate in its measurement of distance. It's the only Footpod that is accurate enough that it doesn't require calibration, something that greatly improves its usability. (It's possible to tweak the accuracy with calibration, but out of the box is should be much better than GPS.) If you look at my testing of distance accuracy you'll see that the Stryd is right at the top of the chart, and is far more accurate than any GPS device I've tested. This accuracy is also reflected in its measurement of current running pace. I think that this feature alone makes the Stryd good value for money. (Stryd doesn't use or provide GPS data, it uses accelerometers. Depending on the watch, the data from Stryd can be combined with the Watch's GPS data so that Stryd gives distance and pace, and the watch's GPS can be used for navigation.)
- Elevation. I suspect that Stryd is providing remarkably accurate elevation information. Due to limitations on data export I've not been able to perform any statistical evaluation, but anecdotally the data looks really good. Obviously, the Stryd cannot provide any absolute altitude information, but it does seem to be able to measure relative changes far better than either GPS or barometric altimeters. At the moment, this information is not as directly usable as I'd like, as it's only available in real time via their, not their watch integration. If you use the Connect IQ data field, it will record elevation as a custom data track, and it is possible to copy this to the standard elevation track using plugins to Sport Tracks.
- Running Power. As I talk about in my page on Running Power Meters, I believe that they are not power meters at all. Like other running power meters, Stryd does not actually measure running power, but attempts to estimate what the power would be based on the things it can measure. My assumption is that it is mostly using pace and elevation change, possibly along with Cadence or Ground Contact Time. As discussed in the section below on the testing running power, I have found that the latest Stryd firmware gives a good estimate of relative intensity. I've been able to use Stryd to better pace myself on hilly runs, as well as giving additional insight into High Intensity Interval Training. The current version of Stryd has "wind detection" to adjust the power estimate based on ambient wind.
- Form Power. Stryd describing this metric as the "running in place power", but it's unclear what that really means more if it has any value. They suggest that a decrease in this value represents improved Running Economy, but there is nothing to back that up.
- Cadence. Cadence is fairly trivial to measure for even a far simpler Footpod, so Stryd nails this easily. It's arguably one of the most important running metrics, so you should pay attention to this. There are far cheaper ways of measuring cadence (like MilestonePod) but it's nice to have this included in the Stryd.
- Ground Contact Time. Ground Contact Time is how long each foot spends on the ground, and it's often suggested that a lower value represents a better Running Economy though the research is mixed.
- Vertical Oscillation. Because Stryd is a Footpod, it has no way of measuring Vertical Oscillation. Therefore, Stryd is estimating vertical oscillation from things like Cadence and Ground Contact Time. My testing shows that Stryd gives a lower vertical oscillation compared with other devices. This is most likely because Stryd is estimating the vertical movement of the runners' center of gravity rather than just the torso, which is a more appropriate and useful measure. Look for Fredrik Zilléns' excellent video "Up/down movement when running is not what it looks like" for more details.
- Leg Stiffness. It's possible to model a runner with their legs representing a spring and the rest of the body as a mass. When a runner lands, they decelerate their bodies vertical movement and the rate of deceleration can be used to estimate the stiffness of the "spring". The stiffness of this hypothetical spring is related to Cadence, with a higher cadence having a stiffer spring. The preponderance of evidence suggests that a stiffer leg stiffness is more efficient, and that fatigue tends to soften the stiffness. There are various ways of estimating leg stiffness, such as measuring the vertical ground reaction force and vertical movement. This gives the force applied and the amount of deformation of the "spring", resulting in a reasonable estimation of stiffness. Another approach is to use ground contact time and cadence, which is how I suspect Stryd is estimating stiffness. Personally, I suspect that this is an overly simplistic model.
Note that Stryd provides no information on foot strike parameters such as pronation, or foot landing position.
2 The Pod
The Stryd pod is similar to other Footpods. It's slightly larger than most, and has an LED status light on the top. Stryd uses a rechargeable battery that they claim lasts about 20 hours. That's good enough for most runners, but may be a problem for longer ultramarathons. Stryd recharges through a small cradle (earlier versions used wireless charging.) Stryd uses a 9-axis sensor rather than the typical Footpod that uses a 3-axis sensor. The Stryd pod weighs 0.32oz/9.1g, compared with the Garmin Footpod at 0.34oz/9.6g, and the rather oversized Polar Footpod at 1.0oz/28.1g. Stryd doesn't provide any details of the waterproof rating of their pod. Stryd claim IP67 waterproofing, which is safe for submersion to 1 meter. However, that means that you can't run through water as the pressure due to foot movement will exceed the pressure. That would mean taking the pod off if you're going through water that will cover the pod, though I suspect you should be okay if you walk through slowly.
3 Footpath Visualization
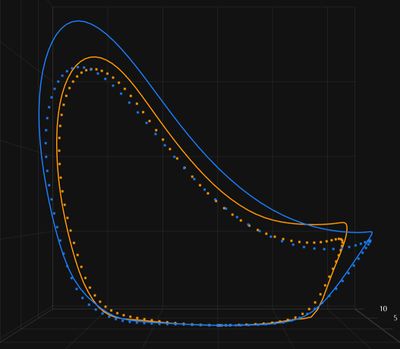
The latest versions of Stryd support "Footpath Visualization", which shows how your foot moves during the running cycle. Two Stryd pods gives you both feet, but the latest version supports this visualization with just one pod (obviously showing only one foot.) You can show your footpath for a specific run, but I find the ability to show your average footpath for a month at a given pace to be the most useful. Below you can see the comparison between October as a solid line and September as a dashed line (blue is right foot). This is my footpath for running between 3:53-4:02/Km, and you can see my right foot is going higher than my left.
Things become more dramatic when viewed from the rear, where you can see my left foot is going a lot wider than my right foot, and the problem has become worse. This is something I can work on, looking for flexibility and strength asymmetry.
The main thing that's missing is the ability to compare your footpath to other runners. If you could show how your footpath looks compared to the much fitter runners when your pace is similar, you would probably see areas for improvement.
4 Stryder Distribution
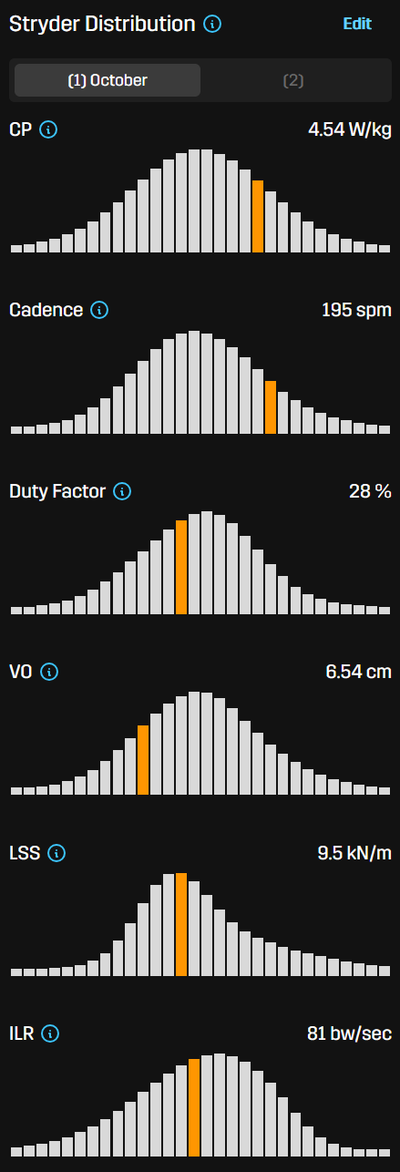
I find the "Stryder Distribution" graphs to be a useful way of evaluating how my running form compares to other runners. It shows where you are on a distribution curve against runners of different age categories, and more importantly, at specific paces. Below is the graph comparing me to all age ranges while running at 3:25-3:35/km pace. You can see my Cadence is higher than average, probably because my stride length is limited and I'm having to use a faster cadence to reach that pace. My duty factor, which is the percentage of time in contact with the ground, is lower than average which is good, but might be due to my high cadence. My Vertical Oscillation (VO) is quite low, which shows my leg swing and bounce are both good. Leg Spring Stiffness is average, so there's room for improvement with strengthening my leg muscles. Impact Loading Rate is a little lower, showing I'm not jarring on landing. So, you can see how these distributions can show you where to improve your running. It would be nice if Stryd would give a comparison based on Critical Power, so you could compare with faster, fitter runners. I'd love to know how elites run at slow paces, and how their slow pace compares with mine.
5 Power to Heart Rate
The relationship between your heart rate and your power output tells you how fit you are. This metric, HrPwr, will go up as your fitness improves. Your HrPwr will also change during a run, with fatigue, dehydration, and Glycogen depletion all reducing your HrPwr as your heart rate drifts upwards.
6 Testing Running Power Estimate
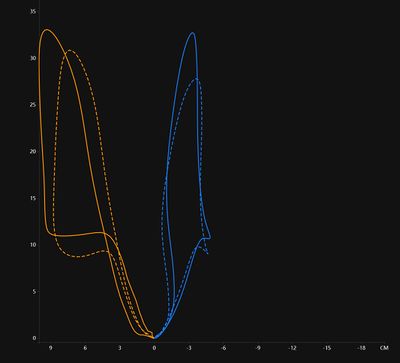
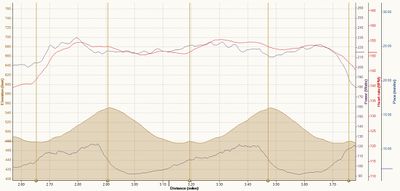
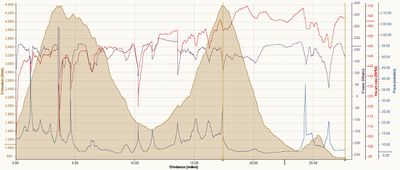
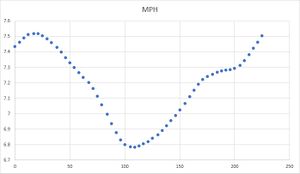
It's important to realize that Stryd is not a Power Meter in the way that cyclists have power meters. Stryd does not measure power in direct, absolute terms, but creates a mathematical estimation based on running pace and incline (and possibly other factors.) This means that you can't easily use Stryd to evaluate improvements in running form or Running Economy, though looking at the power estimate against heart rate might give some interesting insights. However, I've found Stryd's power estimate to be quite useful in the real world. It allows for far more accurate pacing over undulating terrain than pace or heart rate. It can be a bit of a shock to see just how slow you have to go uphill to maintain an even effort! Earlier versions of the Stryd firmware tended to dramatically underestimate the effort of running downhill, but as of 1.1.2, the estimate seems far better. The graphs below are showing my runs up and down a local hill. It's not a very long Hill, but it is fairly steep, averaging 6% with sections nearer 10%. In these tests, I'm aiming to keep an even effort based on the Stryd power estimate. You can see that not only is the Stryd power estimate reasonably stable, but so is my heart rate, indicating that the Stryd estimate is doing a remarkably good job across dramatically different inclines. Though this is still a modeled, estimated power intensity, it's far better than anything else available to us and is good enough for real world usage. If you need to accurately pace yourself on undulating terrain (Boston marathon anyone?) Then I'd heartily recommend using Stryd. Of course, you'll need to work out what your estimated power level should be in order to match your target race time, and this is something you'll have to do by trial and error. Simply run a course of the mirrors the race terrain and compare your average pace to your target pace. If you're too slow then your power target will need to be a little higher, and vice versa.
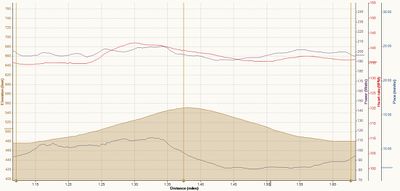
Another use of Stryd is in interval training. For most traditional intervals, where you're performing them on the flat (e.g. a track) then using pace is probably best. However, for Hill training, Stryd will give you a much better idea of your intensity than pace or heart rate. The graph below shows me running hard up the hill, then resting on the way back down. You can see that both my heart rate and power estimate rise on the uphill and decline on the downhill. You'll notice that my heart rate response is rather slower to the change than the power estimate, making it more useful for providing a useful, real-time estimate of intensity.
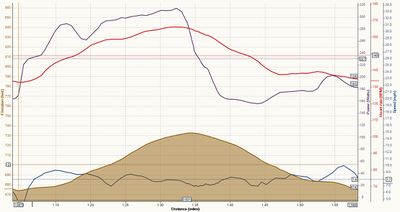
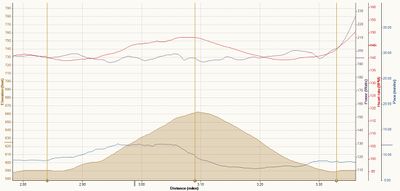
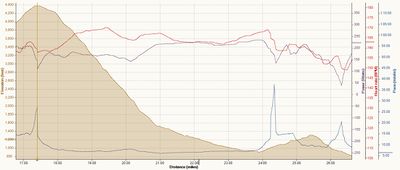
I've found Stryd to be particularly useful in High Intensity Interval Training, especially when using the Polar V800 that has a native power support. With the V800, I can set the watch to display the maximum power for the current lap, which gives me a far better idea of how hard I'm pushing it on each interval than is possible any other way. You can see in the graph below that in short HIIT intervals the heart rate is a lagging behind power estimate, and my heart rate is still rising after I've slowed up.
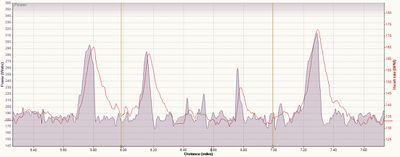
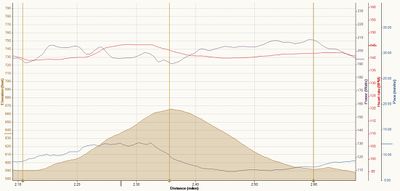
Below is an example from another runner during a marathon plus, mountainous training run. I've applied a lot of smoothing to the heart rate and power data, then scaled and aligned the two tracks. Over the first mile or so you can see the resting heart rate, rise up as of a warm-up, then the heart rate and power match reasonably well up and over the first hill, again suggesting that the Stryd power estimate is probably reasonable. For the second half of the run, you see heart rate rising above the power track, which I believe is an indication of Heart Rate Drift, probably due to heat and dehydration. This shows one of the benefits of even a broad approximation of power compared with using heart rate for longer training runs.
However, it's also in indication of some of the weaknesses of mathematically estimating our rather than measuring it. If we look at the steep descent on the second hill, it looks like there is still some underestimation of power. The other possible issue is that Stryd is estimating for a typical runner, and each person's efficiency under different conditions is likely vary quite a bit. It's important to remember the limitations of this type of estimation, and avoid confusing it with what you'd get from a power meter.
6.1 Analysis of Power Estimate
I've not performed any statistical analysis of Stryd's power estimate, mostly because I can't work out a reasonable way of doing this. Ideally, I'd be able to compare Stryd's power estimate with VO2 measurements from respiratory gas exchange, but I don't have the equipment, nor is it likely to be practical. The approach I've used above is to compare Stryd's power estimate with heart rate, but while heart rate is a well-established method of measuring exercise intensity, it's flaws (as noted in detail below) me know that he can only be used for relatively short periods of steady state exercise. (I'm hoping that someone will come up with a portable VO2 meter that will measure oxygen and carbon dioxide in your breath.)
7 Watch Support
Stryd has support for a remarkable number of running watches. It supports both Bluetooth and Ant+, and it can look like a standard Footpod, a cycling power meter, or provide more sophisticated data. There are a large number of combinations of watches and configurations to consider, so I'll look at the general integration approaches and then look at specific watches.
7.1 Types of Watch Integration
- Footpod. Stryd can send standard Footpod data over both Bluetooth and Ant, giving the usual distance, pace, and cadence data. You can use it like this to get accurate distance, pace and Cadence data into the vast majority of watches I've tested. However, only a few watches will support this while recording a GPS track, and so most will need to be in indoor/treadmill mode. This means there's two modes to consider:
- Footpod with GPS. This is the ideal mode; you have your watch get all distance and pace data from Stryd, while still recording a GPS track. This will allow you to show where you've run, enable any navigation like back to start or breadcrumbs, and for things like Strava segments.
- Footpod without GPS. If your watch doesn't support the above "Footpod with GPS" mode, you have to set it to running indoors or treadmill mode where you lose all the GPS data. This works, but may not be what you want. (For watches that support Connect IQ, there is the option of using the "Stryd Race" app which will record GPS data along with Stryd data, but the features are a little lacking at the moment.)
- Footpod with Power in Cadence. Note that Stryd used to be able to transmit the power estimate in the cadence field, but this feature has been removed.
- Native Power. Some watches will support the use of Power natively in running mode, rather than just in Cycling mode (see below.) This is a great option as it usually allows for displaying power in different ways, such as the average over several time periods, such as 30 seconds or the lap. This mode also allows for things like run or lap maximum power, which I really like for High Intensity Interval Training. Usually you also get the power data exported for analysis in other software, like Golden Cheetah.
- Cycling Power Meter. Stryd can send the same data that a cycling power meter would, so any watch that supports the cycling power meter will support stride in the same way. This gives some good support for power, and in indoor cycling mode you should be able to get pace, distance, and cadence data from the stride as well. There are a few annoyances with this approach, the biggest one being that you get your speed in MPH or KPH rather than min/mile or min/Km which would take some getting used to if you're a runner that used to thinking in terms of pace rather than speed. The other annoyance is that all of your data files will be considered as cycling rather than running, which could confuse your training log.
- Connect IQ. The advantages of Garmin's Connect IQ are shown in the ability for Stryd to add their sensor to any Garmin watch that supports Connect IQ. If you install the Stryd Connect IQ data field, it will show the power estimate, as well as recording all of the Stryd data into the fit file. Using this data field does not stop you using the Stryd as a normal Footpod at the same time. Because the Connect IQ only gives you the power, you still have two modes of Footpod integration, giving you two modes:
- Connect IQ + Footpod with GPS. The perfect solution; you get all the Stryd data, the distance/pace accuracy, and GPS for navigation.
- Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS. On the lower end Connect IQ enabled watches you have to set them to indoor/treadmill mode, so you get all the Stryd data, the distance/pace accuracy, but you don't have any GPS data.
Here's another way of looking at the options. I've ranked them in the order I'd use them, which is accurate pace & distance is the most important thing, then having GPS tracks for navigation, then having the power estimate, and lastly having the extra Stryd data.
| Type | Stryd Pace & Distance | GPS | Extra Stryd Data | Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Native |
| Connect IQ + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Connect IQ |
| Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | Yes | Connect IQ |
| Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Power Only | No | Yes | No | Native |
| Cycling Power | No | Yes | No | Cycling Only |
| No Support | No | No | No | No |
- Stryd has a Connect IQ application that will record GPS data along with Stryd data, but the functionality is a little limited right now.
7.2 Watch Specifics
Here's a mapping of the modes above to specific watches. In all cases, I've prioritized accurate pace/distance information over either GPS data or the power estimate. I've put the detailed notes of how to pair Stryd with specific watches and how well they work at the bottom of this page.
|
Watch |
Stryd Support |
Stryd Pace & Distance |
GPS |
Power |
Extra Stryd Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polar V800 Review | Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Native | No |
| Suunto Ambit2/Ambit2 Sport | Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Native | No |
| Suunto Spartan Ultra Review | Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Native | No |
| Suunto Spartan Trainer Review | Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Native | No |
| Garmin Fenix 3 Review | Connect IQ + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin 935 Review | Connect IQ + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin Fenix 5X Review | Connect IQ + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin 920XT Review | Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS* | Yes | No | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin Vivoactive Review | Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS* | Yes | No | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin Vivoactive HR Review | Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS* | Yes | No | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin 235 Review | Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS* | Yes | No | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin Epix Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Polar M430 Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Polar M400 Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Suunto Ambit3 Run Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Suunto Ambit2 R Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Garmin Fenix 2 Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Garmin 620 Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Garmin 225 Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Garmin 910XT Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Garmin 310XT Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Garmin 610 Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Leikr Review | No Support | No | No | No | No |
| Epson SF-810 Review | No Support | No | No | No | No |
| Epson SF-510 Review | No Support | No | No | No | No |
| TomTom Cardio Runner Review | No Support | No | No | No | No |
7.3 Bluetooth or Ant+
Stryd supports both Bluetooth and Ant+, and both work well. Bluetooth has the limitation that you can only have one receiver talking to Stryd at a time, so you can't have it linked to two different watches simultaneously, or to a watch and your smart phone at the same time. (I have had occasions where the Stryd has stayed linked to my smart phone, so I've had to turn off Bluetooth on my phone to allow Stryd to link to a watch.) With Ant+ you can have as many watches linked simultaneously, and it's possible to have Stryd linked to both one Bluetooth watch and several Ant+ watches at the same time. If you're using Garmin Connect IQ, you can have Stryd work as both a standard Footpod and connected via the Connect IQ data field.
8 Calibrating Stryd
My testing shows that Stryd is remarkably accurate, but the company has reported that there can be some variation between Stryd devices. If you'd like to check your calibration, I'd recommend this process. (Note that the Suunto Spartan watches don't allow for any calibration.)
- Check that your watch is set to get pace and distance from Stryd. The best way I've found to verify this is to set the calibration factor to 0.5 and go for a short run. It will be immediately obvious that your pace is only half what it should be.
- Check the calibration factor is set to 1.0, and that any auto calibration is disabled. Auto calibration uses GPS, which is going to be far less accurate than Stryd. (If you're verifying a previous calibration, leave it set to that value but remember to adjust in the final calculations.)
- Use a standard 400 m oval track at a time when you're confident you can run in a single lane for a number of laps. The accuracy of a 400m track should be more than adequate for calibration, but if you're interested in the details, tracks are built in the US to various levels, with level 4 being suitable for national collegiate events.
- You should run approximately 30cm/12" from the inside edge of the lane, not down the middle. For the first lane, running along the inside marker will reduce the distance by ~1m, running the outside edge will increase the distance by ~3m, and running down the middle will increase the distance by ~1m.
- You don't have to run down the first lane, but you have to adjust your distances for lanes that are farther out. (See table below.)
- Start your watch and start running some distance before the start line. I would suggest at least 100 m. This is partly because the stride will do some smoothing, and obviously when you're run starts you're going from stationary to running. However, I've also noticed a number of watches that can be slow to start recording, so there first lap is rather short. You'll need to discard this first lap.
- Run a number of laps hitting the lap marker as you parse the start, or some other landmark.
- After the run, look at the lap distances for the measured laps, ignoring the first. The calculation is then fairly trivial; divide the actual lap distance by the average lap distance to give your calibration factor.
| Lane | Total length |
|---|---|
| 1 | 400.00 m |
| 2 | 407.67 m |
| 3 | 415.33 m |
| 4 | 423.00 m |
| 5 | 430.66 m |
| 6 | 438.33 m |
| 7 | 446.00 m |
| 8 | 453.66 m |
| 9 | 461.33 m |
Don't use a race to calibrate, as it typically very difficult to precisely run a straight line and hit the tangents perfectly. You can also have problems with start up on some watches, where it doesn't record the first few seconds of the run.
8.1 Example Calibration Data
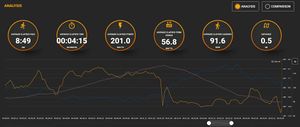
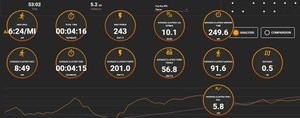
I ran a calibration test on a university track, running in the third lane with my Stryd on the inside (left) foot. I not only wanted to validate the calibration, but I also wanted to check the stability across a range of paces, so I gradually increased my speed on each lap. My previously calculated calibration was 1.013x (or 101.3% in my Garmin) and the average error was 100.15%, so my new calibration was 1.013 / 1.0015 = 1.011507, which works out to 101.2% on my Garmin.
| Distance (m) | Ratio | Error | Avg Pace | Best Pace |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 414.8 | 0.998724 | -0.53 | 9:40 | 8:17 |
| 414.1 | 0.997038 | -1.23 | 9:40 | 9:13 |
| 416.7 | 1.003299 | 1.37 | 9:14 | 8:59 |
| 414.8 | 0.998724 | -0.53 | 8:59 | 8:24 |
| 416.3 | 1.002335 | 0.97 | 8:33 | 8:17 |
| 414 | 0.996798 | -1.33 | 8:31 | 8:09 |
| 415.8 | 1.001132 | 0.47 | 8:03 | 7:49 |
| 417.4 | 1.004984 | 2.07 | 7:46 | 7:34 |
| 417.2 | 1.004502 | 1.87 | 7:31 | 7:21 |
| 415.5 | 1.000409 | 0.17 | 7:12 | 7:00 |
| 416.4 | 1.002576 | 1.07 | 6:46 | 6:32 |
| 417.2 | 1.004502 | 1.87 | 6:34 | 6:18 |
| 417.9 | 1.006188 | 2.57 | 6:10 | 5:51 |
| 415.1 | 0.999446 | -0.23 | 5:41 | 5:02 |
9 The Stryd App
The Stryd app is rather limited, and I mostly use it just to sync data with the web site. It is needed for use on a treadmill. See below under "smartphone apps" for more details.
10 The Web Site
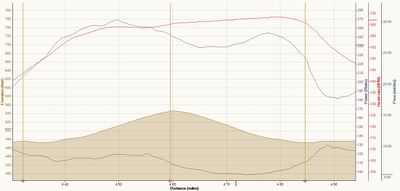
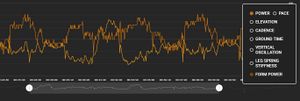
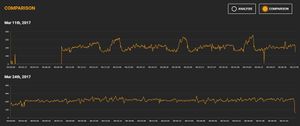
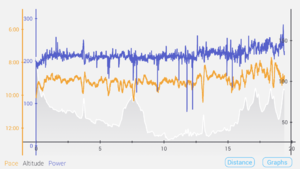
I rather like the Stryd website. There's the usual calendar views of your runs, but there is some useful analysis you can do within their website. The biggest shortcoming I've found is that you can only show data by time, not by distance. If you look at the first graph below the hill shown by the purple line looks asymmetric because I'm going down much faster than I'm going up.
This view allows you to overlay various metrics in a different colors. Here you can see one of the hill repeats I analyze further down this article, so I have elevation, power, and pace shown. You'll also see some average values in the circles above the graph. If you look at the very bottom of the image you can see a slider where you can zoom in on a subsection of a run. Here I'm showing you just one he'll repeat.
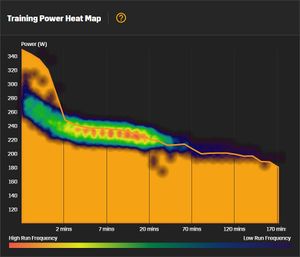
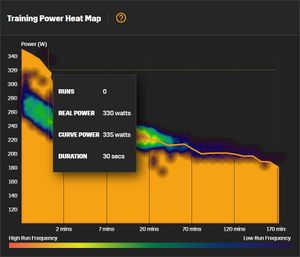
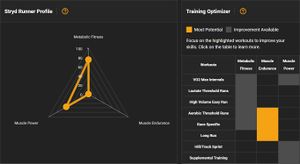
Stryd have added some analysis on their web site that looks at your overall training history. The heatmap is certainly fascinating, though I'm not sure how useful it is. It shows the highest power estimate you've run at for various times. The color then shows the how often you've achieved a power estimate/time combination. If you mouse over the line, you can see a popup with the details. You can see my curve is fairly flat, indicating my training intensity doesn't very much, which is what I'd expect given most of my training is Long Runs. I'm not sure how to interpret the Stryd Runner Profile or how it's calculated.
11 Connect IQ Data Field
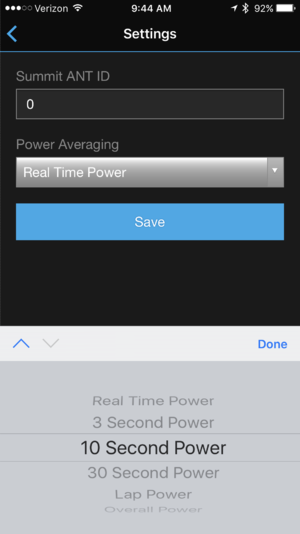
The Connect IQ Data Field for Stryd will show power on a Connect IQ compatible Garmin watch. This doesn't interfere with using Stryd as the footpod at the same time, which is important. The Data Field will record not only power, but the other metrics like Ground Contact Time and the display is configurable to show power averaged over various time periods, lap average, or overall power for the run. Of course, you can only have one field configured, so you can't see both current power and lap average for instance. You also don't get alerts based on power value.
12 Data Analysis
Because Stryd is compatible with so many watches, it's fairly easy to get most of the data into an app for analysis.
- Pace and Distance. If you have your watch set to take a distance from the Stryd, you'll naturally have access to distance in pretty much any application you can get your data into. Because you have accurate distance, you should have accurate pace to analyze as well.
- Running Power. There's some analysis in the Stryd web site, but most users will want to export the data into another application. Getting power into such an application for analysis will depend on which watch you are using and how you got it configured.
- If you're using an Ambit 2/3 with native power support, you get power in the exported FIT files normally.
- For the Polar V800 there doesn't seem to be support for exporting the power in the TCX file. Hopefully they'll fix that soon.
- If you're pretending this is a cycling power meter, then everything should work just as it would for cycling power, but of course it looks like a cycling workout.
- If you're using the Garmin Connect IQ data field, then you'll need to have an application that supports importing customer data. I found that Golden Cheetah worked fine, as does SportTracks with the Custom Data Tracks plugin and the Garmin FIT plugin.
- Cadence. Cadence is well supported by pretty much any analysis application, unless of course, your using the cadence field for power. Note that the Garmin Connect IQ data field will record the cadence value from the Footpod in addition to any other Cadence device.
- Elevation. I've found it tough to get elevation data into an analysis application. I'll update you if I find a good way of doing this.
- Form Power, Ground Contact Time, Vertical Oscillation, Leg Stiffness. These fields are all available via the Garmin Connect IQ data field, and can be viewed using Garman Connect.
13 Stryd and Running Economy
One advantage of Stryd is that it's power estimate can be used to then estimate Running Economy and Heart Rate Drift. You can read more about this at HrPwr.
14 Testing Distance and Pace
I tested the distant accuracy of the Stryd using the same basic methodology as I do for my GPS Accuracy testing. (See GPS Testing Methodology for details.) I used a Polar M400 configured to use the distance from the Stryd footpod. As you can see from the results, the Stryd is remarkably accurate, far better than any GPS device I've tested. My testing of pace is more anecdotal, but I've been able to hit my target paces using guidance from my Stryd. I've tested using a range of paces from 10:00 min/mile to 6:30 min/mile and the Stryd allows me to cover a given distance in just the right time.
14.1 Accuracy on Single Track Trails
My GPS Testing Methodology uses an asphalt/tarmac path rather than technical single track trails. This has raised the reasonable question of how Stryd would perform on more challenging terrain. To find out, I measured a section of what I will consider semitechnical singletrack. I used a surveying wheel, as my mountain biking skills are not up to using the US ATF certification process, and I'm not sure that that process would really work in this environment anyway. Measuring singletrack is a little challenging, but I was able to get consistent results from repeated measurements using the survey wheel to within a few inches. The trail I used is quite twisty, and has sections where I'm barely running, and my overall pace was about 11:00 min/mile rather than the 8:00-8:30 pace that I'd be maintaining on asphalt. Hopefully this gives a sense of the difficulty of the trail, and you can see a couple of images below. It's certainly not a truly technical singletrack where I'd be rock hoping, but it's also a trail where it's often difficult to get into a rhythm because of having to watch foot placement. I compared the Stryd with one of the most accurate GPS watches I've tried, the Polar V800. I'd never normally tried to measure a GPS device on the trail this twisty, as it just too challenging.
| Accuracy (Combined) |
Trueness (Average Distance Error) |
Precision (From mean) |
Precision (From true) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stryd | 1.42% | 1.19% | 1.09% | 1.62% |
| Polar V800 | 12.55% | 12.42% | 1.99% | 12.68% |
As you can see, the Stryd does remarkably well, even on this challenging singletrack. It's more accurate than the Polar V800 would be on asphalt, which is quite an achievement. To put this into perspective, the best GPS watch, the Polar V800, had an appalling level of inaccuracy on the same course. I expected GPS to be a lot worse on this type of challenging terrain, but even I'm surprised by this level of problem.
14.2 Accuracy Walking
I've not done any statistical analysis of the accuracy of the Stryd while walking, mostly due to time constraints. However, my anecdotal use of Stryd while hiking on my testing course suggests that it's equally accurate when hiking in boots as it is when running.
14.3 Accuracy and Consistency at Different Paces
My testing showed that Stryd remains consistent across a wide range of paces. I tested from 9:40 min/mile to 5:40 min/mile with no differences.
14.4 Responsiveness
Stryd seems reasonably responsive to changes in pace, though it's hard to determine how the smoothing of Stryd interacts with any smoothing of the watch. I've found Stryd responds within a few seconds, though the power estimate is a little slower to adjust. Recent firmware updates have improved the responsiveness of the power estimate, though it's still a little slower than I'd like on rapidly changing slopes.
15 Treadmill Problems
The Stryd is so accurate outdoors, I couldn't understand why it was so bad on a treadmill. To my chagrin, I discovered that the main problem is my treadmill speed display is way wrong. Accurately calibrating a treadmill proves to be rather more complex than I'd have expected, as the treadmill will slow down when your foot is in contact with the belt, then speed up when you're in the air. For details on how to evaluate your treadmill have a read of Treadmill Calibration. However, this variation makes it tricky to know what the "true" speed should be. Obviously, the average speed of the belt is completely wrong, as the speed of the belt while your airborne has nothing to do with your running speed. During the time your foot is in contact with the belt, should you use the minimum speed, the average speed or the maximum speed? With my treadmill, the difference between minimum and maximum during contact is about 15%, and between average and minimum is about 9%. I've found Stryd seems to be quite close to the minimum speed rather than the average during contact. I calibrated my treadmill and then calibrated Stryd to the corrected treadmill speed, which is a lot of effort and tricky to get right. A much simpler solution is to use the North Pole Engineering Runn Treadmill Sensor, which measures the treadmill speed with far less effort and greater accuracy.
16 Testing Battery Life
I've not done a single long run that would allow me to test the battery life for an ultramarathon. However, on multiple shorter runs (25-120 minutes) I found that Stryd was reporting 10% battery life left after 5.5 hours, which is far short of the claimed 20 hours' battery life. However, this may well be due to one of the many watches I have paired to Stryd keeping the pod alive well after the run, plus I tend to pair my Stryd to different watches many, many times. I will attempt some more realistic testing in the near future. I've seen one report of an ultrarunner who completed 100-miler in 28 hours and had 27% battery life. This is anecdotal, but encouraging.
17 Stryd For Ultrarunning?
The claimed battery life for Stryd is only 20 hours, which is not long enough for many ultramarathons. Obviously, if you could have two Stryd pods, but that would be expensive. One option would be to use a Garmin watch that supports UltraTrac to extend the battery life along with the Stryd for accurate distance and pace. This would last for around 20 hours, and when the Stryd battery is dead, things would fall back to GPS. You may even be able to switch to normal GPS mode mid-run. I found that this worked nicely on a short run when I tested it out with the Garmin Fenix 3. I started off with the watch in UltraTrac mode and the Stryd connected. I then took the Stryd pod off to simulate the battery running out, and swapped to normal GPS mode.
18 Stryd Internals
For those that are interested, here are the internals of a Stryd. (Thanks for Paul Day for the photo and the willingness to do the work.)
19 Stryd and Critical Power
The Stryd app has started to support Critical Power, a concept more widely used in cycling. The Stryd method of calculating Critical Power is to use one of 5Km/10Km race time, or a test protocol using just two durations. The research I've found on Critical Power suggests that more data points are needed to provide a valid measure of Critical Power, and especially W' (anaerobic work capacity). Most research uses a fixed power output to exhaustion rather than a time trial. A time trial includes aspects of pacing and skill, so this seems a poor substitute. (Typically, CP tests define "exhaustion" as when cycling cadence drops below 50 RMP.) I'd recommend using more test runs and using one of the many Critical Power calculators available online. Stryd also has an automatically calculated Critical Power, but I've not seen any independent validation.
20 Stryd's Power Estimate Compared with Cycling Power
I performed an incremental test with both Stryd for running and my Tacx Neo 2 for cycling. For running, I used a 400m track, increasing my pace from 10:00 min/mile to 5:30 min/mile over 14 laps. I then performed a similar test cycling, increasing the power gradually. I then mapped the power from each to my heart rate. In both cases I found a reasonable linear relationship between power and heart rate. Using the linear relationship, I found that Stryd power is generally quite a bit higher than Cycling power. For me, Stryd Power = (Cycling Power + 40) / 1.13, so 100w in Stryd is about 70w Cycling.
21 Using Stryd With Your Watch
Here's my notes on the compatibility testing I've done so far. I've had occasional issues with devices connecting to Stryd at the beginning of a run. I've not found any pattern to this, and it seems to impact both Bluetooth and Ant+ devices, so make sure you have a connection before starting your run. I've also occasionally forgotten to turn off auto-calibrate, which is another gotcha.
|
Watch |
Stryd Support |
Stryd Pace & Distance |
GPS |
Power |
Extra Stryd Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polar V800 Review | Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Native | No |
| Suunto Ambit2/Ambit2 Sport | Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Native | No |
| Suunto Spartan Ultra Review | Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Native | No |
| Suunto Spartan Trainer Review | Native Power + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Native | No |
| Garmin Fenix 3 Review | Connect IQ + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin 935 Review | Connect IQ + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin Fenix 5X Review | Connect IQ + Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin 920XT Review | Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS* | Yes | No | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin Vivoactive Review | Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS* | Yes | No | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin Vivoactive HR Review | Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS* | Yes | No | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin 235 Review | Connect IQ + Footpod without GPS* | Yes | No | Connect IQ | Yes |
| Garmin Epix Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Polar M430 Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Polar M400 Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Suunto Ambit3 Run Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Suunto Ambit2 R Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Garmin Fenix 2 Review | Footpod with GPS | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Garmin 620 Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Garmin 225 Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Garmin 910XT Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Garmin 310XT Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Garmin 610 Review | Footpod without GPS | Yes | No | No | No |
| Leikr Review | No Support | No | No | No | No |
| Epson SF-810 Review | No Support | No | No | No | No |
| Epson SF-510 Review | No Support | No | No | No | No |
| TomTom Cardio Runner Review | No Support | No | No | No | No |
21.1 Garmin Fenix 3, Fenix 5X, 935
For the Garmin Fenix 3, Garmin Fenix 5X, Garmin 935:
- Pair as a normal footpod. Settings -> sensors -> add new -> footpod. Under the sensor, set speed=always, distance=always, calibration -> auto calibrate disabled. (There's a full description of the process for the F5X on the review page.)
- These watches have the best Stryd support, but note that Garmin has abandoned the Epix, so there's no firmware updates.
- The Connect IQ data field gives power display, and it records all the other Stryd data like Ground Contact time.
- Pair the Fenix 5X/935 via Ant+, not Bluetooth for the Connect IQ to work.
- You can set the speed and distance to always come from the footpod so you still get GPS. This is obviously important for navigation and the mapping features of the 5X, which is a key reason for it over the 935.
- These watches support Stryd for cycling power, but I wouldn't use that unless you want alerts for power being out of range.
- I found some smoothing and rounding of the pace data, but not much.
- Occasionally I'll find the watch won't detect the Stryd at the start of the run. In those situations, I have to go into settings, sensors, Stryd, and select "connect", which time the watch connects fine and the connection persists when I go back to start the activity.
- Power data can be exported to tools like Golden Cheetah by exporting the FIT file from the Garmin web site (activity page, click on the cog icon on the top right, select "export original").
- Warning: there are credible reports that the Fenix 5 and 5S (but not the 5X) have Ant+ connectivity issues. I'd recommend connecting them as Bluetooth Footpods, which means you will not get the Connect IQ support.
21.2 Polar V800, M400, M430
For the Polar V800, Polar M400, Polar M430:
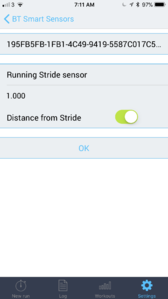
- Pair as a normal footpod. Settings -> General Settings -> Pair and Sync -> Pair Other Device -> select Stryd. Then go to Settings -> Sports profiles -> Running -> Stride Sensor. Calibration=manual, factor = 1.0, sensor for speed=Stride Sensor.
- Note: I have the V800 working with both Stryd and a heart rate monitor (except Wahoo).
- Remember this is using Bluetooth, so if you have a problem it might be because the Stryd is still linked to your phone.
- You can set the M400/M430/V800 to give distance and pace from footpod, while recording GPS tracks. The menu just says "speed source" but it sets distance as well. The menu talks about "stride sensor" as that's what the Polar footpod is called.
- There's less smoothing of pace in these watches compared with others, so the display is nicely responsive. (I know from alpha testing other devices that the M400 actually has pretty much no smoothing at all.)
- There's no cycling power support in the M400/M430, or other native power pod support.
- For the V800 there is native support for Stryd as a power device. You don't need to pair Stryd as two separate devices (foot pod & power pod), just pair once.
- V800 Power data can be exported to tools like Golden Cheetah by exporting the TCX file from the polar web site. From the activity page, select "export session", then choose TCX.
21.3 Garmin 920XT, Vivoactive, Vivoactive HR, 235
For the Garmin 920XT, Garmin Vivoactive, Garmin Vivoactive HR, Garmin 235:
- Pair as a normal footpod.
- 920XT: Settings -> sensors -> add new -> footpod. Under the sensor, set speed=always, calibration factor -> auto calibrate disabled, factor=100.0.
- Connect IQ gives power display, and it records all the other Stryd data like Ground Contact time.
- Power data can be exported to tools like Golden Cheetah by exporting the FIT file from the Garmin web site (activity page, click on the cog icon on the top right, select "export original").
- You can't get distance from Stryd with GPS active, which means you have to run in indoor/treadmill mode. (The 920XT/235 can have pace from Stryd with GPS, but not distance).
21.4 Garmin Epix
For the Garmin Epix:
- While the Epix supports Connect IQ it doesn't support the latest version, so it can't use the Stryd Connect IQ apps.
- Pair as a normal footpod. Settings -> sensors -> add new -> footpod. Under the sensor, set speed=always, distance=always, calibration -> auto calibrate disabled. (There's a full description of the process for the F5X on the review page.)
- You can set the speed and distance to always come from the footpod so you still get GPS. This is obviously important for navigation and the mapping features of the 5X and Epix are key reasons for buying those watches.
- There is the option of using the Epix in cycling mode to get power from Stryd.
- I found some smoothing and rounding of the pace data, but not much.
- Occasionally I'll find the watch won't detect the Stryd at the start of the run. In those situations, I have to go into settings, sensors, Stryd, and select "connect", which time the watch connects fine and the connection persists when I go back to start the activity.
21.5 Garmin Fenix 2
For the Garmin Fenix 2:
- Pair as a normal footpod.
- Set the "Foot Pod Speed" to "Always On". I expected this to just provide pace from Stryd, but it actually does distance as well. The GPS track is recorded normally and navigation functions are enabled.
21.6 Suunto Ambit3 (all models), Ambit2 R
For the Suunto Ambit3 (all models), Suunto Ambit2 R:
- Pair as a normal footpod (don't pair as a bike power pod if you're using a higher end Ambit).
- You have to ensure that the sports mode you're using is set to use a footpod. If you don't see the Ambit3 search for a footpod when you start the exercise, you need to change the configuration on the Suunto web site. (I've tested the Ambit3 Run/Ambit2 R versions.)
- With the Ambit3, you need to disable auto-calibration, and the menu is a little hidden. Pair your Stryd, then hit the start button, select "exercise", then choose an exercise that uses a footpod. Ensure that the Ambit3 has found your Stryd, then press and hold the Next button to bring up the Activate menu. If you have a footpod active, there will be an option for disabling auto calibration.
- If a footpod is found, the Ambit3 & Ambit2 will get pace and distance from the footpod and override the GPS data. (This means you can use the Ambit2/3 in the lowest GPS accuracy mode to extend battery life while getting accurate pace & distance from Stryd.)
- If you follow the Stryd instructions for the Ambit3 you'll get power but won't get pace/distance from Stryd.
- The Ambit3 & Ambit2 both do quite a bit of smoothing of pace information, so it's not quite as quick to respond as other some other watches.
- With the higher end Ambit 2/3 (above "Run" models) you can use the Stryd in bike mode and get the power estimate that way. However, I strongly believe that accurate pace and distance is vastly more useful than an estimate of power.
21.7 Ambit2/Ambit2 Sport
- These two watches can support Stryd as both power pod and foot pod at the same time. (You can't do this with the higher end Ambit3 watches as the Bluetooth protocol only allows one connection.)
- Pair as a normal footpod then pair again as a bike power pod.
- You have to ensure that the sports mode you're using is set to use a footpod and the power pod. If you don't see the search for a footpod and/or power pod when you start the exercise, you need to change the configuration on the Suunto web site.
- If a footpod is found, the Ambit2 will get pace and distance from the footpod and override the GPS data. As above, you can use the Ambit2 in the lowest GPS accuracy mode to extend battery life while getting accurate pace & distance from Stryd.
- The Ambit2 does quite a bit of smoothing of pace information, so it's not quite as quick to respond as other some other watches.
21.8 Suunto Spartan Ultra/Trainer
For the Suunto Spartan Ultra, Suunto Spartan Trainer:
- The Spartan watches support Stryd for both the power estimate and the pace/distance while retaining GPS. You have to pair Stryd as a footpod only, not as a power pod, which is a little counterintuitive.
- To pair, scroll up to settings, select connectivity, select pair sensor, select Foot POD, pair to Stryd. Do not pair as a power pod. Then go back to the connectivity menu, select paired sensors, select the footpod, scroll to settings, disable auto-calibration.
- Ensure you are using a sports mode that has the footpod enabled and the power pod disabled.
- Power data can be exported to tools like Golden Cheetah by exporting the FIT file from the Suunto web site (activity page, click on the tools on the right, select "export as FIT").
- There's no calibration provided by the Suunto Spartan.
21.9 Garmin 620, 225, 610, 910XT, 310XT
For the Garmin 620, Garmin 225, Garmin 610, Garmin 910XT, Garmin 310XT:
- Pair Stryd as a normal footpod.
- You can't get distance from Stryd with GPS active, which means you have to run in indoor/treadmill mode.
21.10 Other Watches
- Leikr. I could not get the Stryd to work with the Leikr.
22 Smartphone Apps
I've tried a number of iPhone apps with Stryd, with varying results.
22.1 Stryd iOS App
You need to use the Stryd app to update the firmware, and configure the device. It also is the only way of uploading your runs to the Stryd website for analysis. You can use the that during a run, but it's painfully rudimentary. It displays your pace in min/mile as a decimal fraction, so 8:30 min/mile is shown as 8.5 min/mile. Displaying time as a decimal fraction of minutes is both bizarre and frustrating. The app will display the power estimate, cadence, and distance, but there's no customization of the display, graphs, or any of the other amazing things you can do with such a large display. The main value I see in using the app for recording your runs is when you're on a treadmill, as it's the only option for setting the incline/decline.
22.2 iSmoothRun
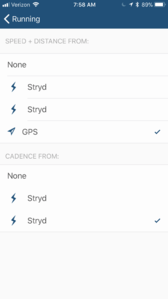
This is one of the better running apps, and has the best support I've found for Stryd. You can set it to take pace and distance from Stryd, and it will successfully use the power estimate. It's not free, but it's well worth the small fee for its functionality. [1]
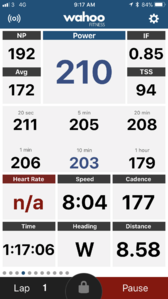
22.3 Wahoo Fitness
The Wahoo Fitness app almost works, and it's free you can get the app to display the power estimate, but only if you have pace and distance set to GPS.
22.4 Strava iOS App
The Strava app won't take pace/distance from Stryd, nor will it use the power estimate. Fail.