Running Power Meters
I've tested many of the running power meters that are currently on the market. While some of them are remarkably useless, some of them can provide value as long as you understand the limitations.
Contents
1 Are They Useful?
Running power meters estimate running power by modeling a runner using inputs such as pace and incline (see below for details.) This means that they are only a rough estimate, unlike cycling power meters that actually measure power directly (again, see below for details.) There's an old saying that "All models are wrong| all models are wrong, but some models are useful." So, while running power meters can't measure your power output, they can still be useful. It's possible for a running power meter to estimate how an incline or decline changes exercise intensity for a given pace. This can allow for more even pacing on hilly courses, which gives a more even effort when training. More importantly, it can allow for more even pacing on a hilly race, which would be great for things like the Boston Marathon. This could be more effective than Heart Rate, which suffers from a significant lag between changes in intensity and a change in Heart Rate, as well as Heart Rate Drift. A running power meter can also be useful when doing uphill interval training, where they can provide some insight into the effort required compared with level ground.
2 Running Power Meters Tested
I've tested a number of running power meters, and they vary vastly in the usefulness.
- The best I've found so far is Stryd which gives some usable estimates of power. It has one of the most accurate estimates of running pace, which is the primary input to a power estimate. I've found it gives a pretty good equivalence between level ground and running uphill, but seems to underestimate a little on the downhill's. However, I suspect there is far more individual variability when running downhill, as different runners will have to break more to keep their pace lower where other runners will be able to speed up more easily. The lag between a change in effort and the Stryd change in our estimation is usually fairly short, measuring only a few seconds. Not surprisingly, it's more responsive to changes in pace than changes in incline, and it doesn't always pick up very well on extremely shallow angles that can still make quite a bit of difference to your running effort.
- Garmin has released their Garmin Running Power as a Connect IQ app that I'm testing now. My suspicion is that this approach will depend largely on the accuracy of the pace measurement. Therefore, I'm expecting pretty useless results from GPS, but more useful information when the Garmin watch is paired with a Footpod.
- The SHFT sensor is fairly useless in its power estimate. It doesn't seem to be able to estimate pace very well, and is particularly useless on the downhill.
- I'm waiting for RunScribe Plus to reach a functional state. So far, it's not stable enough for me to spend time testing it.
- The Garmin Connect IQ platform should allow for alternative models of power, given pace input from an accurate Footpod and the barometer of the watch.
3 How Do They Work?
So far, only RunScribe has been transparent about the model they use for running power, which is available as an online calculator at [1]. Your power output is going to be closely related to your Running Economy, and there's quite a bit known about The Science of Running Economy. The three most important inputs to the model are:
- Weight. A key input to any estimate of running power is your body weight, and generally running effort varies linearly with your weight. This is pretty easy to estimate, or running power systems ask you to enter your weight. I typically enter my approximate body weight and then don't modify it, but you could weigh yourself before each run in your running gear to compensate for additional closing and the like. Of course, it's hard to adjust for hydration changes; in other summer my body weight can vary by 5Lb/2.5Kg over the course of a long run. None of the running power systems evaluate the weight on your feet, which we know can dramatically influence Running Economy.
- Pace. For running, effort varies linearly with your pace across a broad range. Accurately measuring your pace is one of the critical problems in estimating power. Some systems will rely on GPS, but GPS Accuracy is so poor that the systems tend to be deeply flawed. A better approach is a Footpod, and systems like Stryd don't need calibration to produce high accuracy.
- Incline. As everyone knows, running uphill is hard up and running on the flat, so an accurate measure of incline is critical. So far, I'm not aware of any system that using inertial guidance to measure incline. All of the systems rely on a barometer to measure pressure changes. This means they tend to be pretty good when moving up a reasonable incline, but they don't always notice a shallow incline that's still enough to make a difference to the effort required. A bigger issue is understanding the effort required when running downhill, as this is not such a simple relationship between effort and angle. Initially, Stryd did an awful job of estimating the effort of running downhill, but subsequent firmware updates greatly improved this.
There are some other possible inputs, but they appear to be tricky to implement at best.
- Air resistance. RunScribe use height and weight to estimate your frontal surface area to better take into account the contribution of air resistance to the overall effort of running. Obviously, the wind makes a big difference to running effort, especially a strong wind. Unfortunately, it's not practical to measure wind speed on the runner, though the Stryd pattern suggests doing this using a barometer. (I've no idea how that would work, as you need to know direction as well as speed.) Garmin attempts to overcome this by using a cell phone connection and GPS to get the wind speed and direction from the local weather station. This seems like a bad idea to me, as the wind speed and direction at the weather station could be vastly different from where your running. For instance, I typically run on a sheltered Greenway that rarely gets any air movement, even when the weather report is indicating it's breezy.
- Cadence. There is some evidence that Cadence influences running economy, and therefore could be an input to an estimate of running power. However, the research doesn't seem to be well enough and defined that this is easily generalized in a way that would allow it to be modeled.
- Vertical Oscillation. It's intuitively obvious that the up and down movement of your body reduces your efficiency compared with minimal vertical movement. Unfortunately, the science doesn't backup this intuitively obvious observation, and is a relationship between vertical oscillation and running economy is unclear. This is likely to be due to a runner having some elastic properties making them a little more like a bouncing ball. In one study, reducing vertical oscillation reduced running economy, though findings are not consistent.
- Ground Contact Time. There is some evidence that faster runners have lower ground contact time, but the relationship between ground contact time and running economy is mixed at best.
4 Running Power and V̇O2max
A runner's pace is directly and linearly related to their oxygen consumption across a fairly wide range of running paces. And pace is a primary input into running power estimates, which has led some to conclude that the running power estimate is a good substitute for estimating absolute oxygen consumption. This doesn't work for a number of reasons…
4.1 Overall Power
Even if it were possible to accurately measure running power (which it's not), this would still not be a measure of oxygen consumption. Running power is a measure of output, where oxygen consumption is a measure of input. The difference between the two is efficiency, and most of the oxygen you consume running generates heat. You can estimate your power generation from your V̇O2max:
- You can estimate your V̇O2max from a recent race time.
- Given a 3-hour marathon, that would be V̇O2max of ~54 ml/kg/min.
- You can convert oxygen consumption to watts. 1 MET = 3.5 O2 mg/kg/min = 1.16222 W/Kg.
- So, 54*1.6222/3.5 = ~18 W/Kg
- For a 140Lb/63Kg runner (me), that's 1,340 Watts of total output.
Most of that power output is not running power, but goes to generate heat and do other things superfluous to running like keeping my brain working.
4.2 Metabolic Efficiency
The conversion factors used above also only work if you are burning carbohydrate, as fat burning requires significantly more oxygen. It would be wonderful to gain insight into the mixture of fuels that an athlete is burning, but so far, the only way of doing that is to measure the ratio of oxygen consumed to carbon dioxide produced.
4.3 Running Economy
One of the primary benefits of training is likely to be improving running economy, so that you can run faster for the same oxygen consumption. Running economy varies significantly between different runners, which means that running power output would vary for a given oxygen consumption between runners. If a running power meter was actually measuring oxygen consumption, then this would be a way of measuring running economy, but that's an equally flawed idea.
4.4 Comparisons Between Running Power and V̇O2max
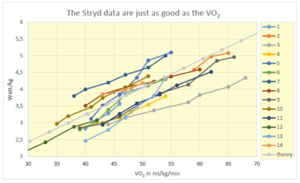
Below is a graph from the book "The Secret Of Running", which compares power output and V̇O2. It's claiming that this shows "the stride data I just as good as the V̇O2." However, this only shows that the Stryd estimate of power varies linearly with pace, which given pace is a primary input to power estimate should come as no surprise. It also shows that oxygen consumption is also linear with pace, something that is well known. However, the power estimate for a given oxygen consumption varies dramatically. You can see for 40 ml/Kg/min, the estimate varies from 2.5 w/Kg to 4.0 w/Kg, a nearly 40% variation.
5 Differences Between Running and Cycling Power Meters
Power meters have become an integral part of training for cyclists, and a number of running Running Sensors claim to have similar benefits for runners. Let's look at the differences between power for cycling and running.
- The amount of energy required to run a given distance on level ground is fairly constant, which means that for runners, pace is often an excellent estimate of effort. By comparison, the effort required for cycling varies with the square of speed and is impacted far more by wind speed and aerodynamics, so speed is fairly useless.
- For cyclists, it's easy to define power output, as it's the energy used to propel the bicycle forward. For runners, it's far less obvious what should be considered power. You could consider it purely to be the horizontal force applied to the ground, as that's the only power that goes towards forward movement, but that's only a tiny fraction of a runner's energy expenditure. Much of a runner's energy expenditure goes to vertical movement, but some of that movement is elastic balance, and some of it requires energy. That means that defining power output for a runner is tricky at best.
- It's quite easy to measure cycling power by measuring the force applied (torque) and the rotation it's applied through. This makes cycling power meters reasonably accurate and not outrageously expensive (compared with say, a metabolic cart that a lab would use to measure oxygen consumption). By comparison, running power is impractical to directly measure and requires a mathematical model with various assumptions that use indirect inputs. This makes running power meters an estimate of power output rather than a true meter. If cycling power meters worked like this, they'd be a wind speed meter that would guess how that influence power output.
- Because running is vastly less efficient than cycling, knowing power output is less important. If a cyclist knows their power output, they have a very good estimate of their exercise intensity. This is because most of a cyclist's effort is delivered as usable power. Even if it were practical to measure running power, it would be of relatively less value due to the influence of Running Economy. This means that a runner is far more interested in their energy expenditure than of their power output.