Difference between revisions of "Running Economy"
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | There are several components that make up running ability, including [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]], and economy. [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]] is the ability of our bodies to generate energy for running and is the focus of a lot of our training. Running Economy is how far and fast you can run with a given amount of energy. Good economy is a critical part of running, and [[Cadence]] is one element I recommend runners focus on. | + | There are several components that make up running ability, including [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]], and economy. [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]] is the ability of our bodies to generate energy for running and is the focus of a lot of our training. Running Economy is how far and fast you can run with a given amount of energy. Good economy is a critical part of running, and [[Cadence]] is one element I recommend runners focus on. (For the financial cost of running, see [[The Cost of Running]].) |
=The Importance of Improving Running Economy= | =The Importance of Improving Running Economy= | ||
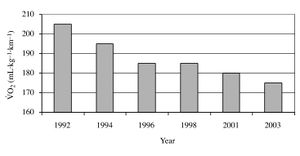
| − | Running Economy can vary by as much as 30% between runners of a similar [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]]<ref name="Daniels-1985"/>. The two charts below show the [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]] and running economy of Paula Radcliffe over a 10 year period<ref name="Jones2006"/>. Over that time Paula Radcliffe's race performance dramatically improved even though her [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]] did not. This suggests that for elite athletes at least, improvements in running economy are critical. | + | Running Economy can vary by as much as 30% between runners of a similar [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]]<ref name="Daniels-1985"/>. The two charts below show the [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]] and running economy of Paula Radcliffe over a 10-year period<ref name="Jones2006"/>. Over that time Paula Radcliffe's race performance dramatically improved even though her [[VO2max|V̇O<sub>2</sub>max]] did not. This suggests that for elite athletes at least, improvements in running economy are critical. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
* '''Cadence'''. The right [[Cadence]] is a key to efficient running and avoiding injury. | * '''Cadence'''. The right [[Cadence]] is a key to efficient running and avoiding injury. | ||
* '''Running Form'''. As well as Cadence, there are other aspects of [[Running Form]] that can improve running economy. For instance, step width can change running economy by 11%<ref name="Saunders-2004"/>. | * '''Running Form'''. As well as Cadence, there are other aspects of [[Running Form]] that can improve running economy. For instance, step width can change running economy by 11%<ref name="Saunders-2004"/>. | ||
| − | * '''High Intensity Interval Training'''. There are | + | * '''High Intensity Interval Training'''. There are several studies that have shown that [[High Intensity Interval Training]] improves running economy. |
| + | * '''Heavy Weight Training and Plyometrics'''. Studies show these interventions can improve running economy by as 4-5%. Heavy weight training is 10 or less repetitions at 70% of 1 repetition maximum, using leg press, squats, etc. Plyometrics are explosive movements, such as Jumps. See [[Plyometrics]] for more details. | ||
=Measuring Running Economy= | =Measuring Running Economy= | ||
| − | In an ideal world, we'd be able to easily measure our [[Running Economy]] and see if things are improving. If we could measure our breath, find out how much O<sub>2</sub> we consumed and how much CO<sub>2</sub> we produce, we'd know how much energy we burned (and from fat or carbohydrate). Such testing would require controlling the time of day, day of the week, diet, and footwear for each test<ref name="Pereira-1997"/> as well as specialist equipment that is not available to recreational runners. Because this is not practical, the best measure we have of energy consumption is our [[Heart Rate]]. This is far from perfect, as [[Heart Rate]] [[Heart Rate | + | In an ideal world, we'd be able to easily measure our [[Running Economy]] and see if things are improving. If we could measure our breath, find out how much O<sub>2</sub> we consumed and how much CO<sub>2</sub> we produce, we'd know how much energy we burned (and from fat or carbohydrate). Such testing would require controlling the time of day, day of the week, diet, and footwear for each test<ref name="Pereira-1997"/> as well as specialist equipment that is not available to recreational runners. (Systems such as Cosmed's K5, PONE, and VO2 Master's VM Pro are becoming available, but cost thousands of dollars. Because this is not practical, the best measure we have of energy consumption is our [[Heart Rate]]. This is far from perfect, as [[Heart Rate]] [[Heart Rate Drift| can vary for other reasons besides supplying O<sub>2</sub> for energy production]]. However, I believe it is a useful approximation and so I developed the simpler "Relative Running Economy." I've created an improved version called "HR-Pwr" which used the power estimate from [[Stryd]] to give a more useful estimate. |
| + | =HrPwr Estimate of Running Economy= | ||
| + | My initial approach was to use heart rate to estimate energy cost and distance covered to measure the effort. This works okay on the flat but is thrown off by changes in elevation. The [[Stryd]] footpod estimates the power output based on pace and elevation changes, which solves this problem nicely. It also gives the possibility of comparing data from running with cycling, though I've found the Stryd power estimate to be much higher for a given perceived effort than cycling. The formula I use is milliwatts per Kg per heartbeat, which I've called [[HrPwr]] (It's available as a [[Connect IQ]] data field.) | ||
=Relative Running Economy= | =Relative Running Economy= | ||
| − | + | This Relative Running Economy calculates a value based on how many heart beats are used for the distance covered. The formula that is shown below and there are more details at [[Relative Running Economy]]. | |
| − | + | Total Beats = (Average [[Heart Rate]] – [[Resting Heart Rate]]) * Time in Minutes | |
| − | + | Work Per Mile = Total Beats / Distance in Miles | |
| − | Total Beats = (Average [[Heart Rate]] – [[Resting Heart Rate]]) * Time in Minutes | + | Efficiency = 1 / Work Per Mile * 100,000 |
| − | Work Per Mile = Total Beats / Distance in Miles | ||
| − | Efficiency = 1 / Work Per Mile * 100,000 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Note that the difference between Heart Rate and [[Resting Heart Rate]] is used to calculate the heart beats used for movement. Ideally the Heart Rate for standing would be used, but typically Resting Heart Rate is taken seated or lying down. | Note that the difference between Heart Rate and [[Resting Heart Rate]] is used to calculate the heart beats used for movement. Ideally the Heart Rate for standing would be used, but typically Resting Heart Rate is taken seated or lying down. | ||
=How to use Relative Running Economy= | =How to use Relative Running Economy= | ||
| − | The calculated Relative Running Economy cannot easily be used to compare different runners. It can be used as to track how your running economy is improving over time, though it is also influenced by changes in fitness. Over the weeks and months of training your Relative Running Economy should gradually improve. For instance, I've seen my RRE go from 110-120 to 130-150 over a period of a few months. Sadly, I've also seen my RRE drop when I put on body fat (see [[Weight Loss and Performance]].) This evaluation of my fitness this proved to be remarkably useful to me. | + | The calculated [[Relative Running Economy]] cannot easily be used to compare different runners. It can be used as to track how your running economy is improving over time, though it is also influenced by changes in fitness. Over the weeks and months of training your Relative Running Economy should gradually improve. For instance, I've seen my RRE go from 110-120 to 130-150 over a period of a few months. Sadly, I've also seen my RRE drop when I put on body fat (see [[Weight Loss and Performance]].) This evaluation of my fitness this proved to be remarkably useful to me. |
=Relative Running Economy to detect Glycogen Depletion= | =Relative Running Economy to detect Glycogen Depletion= | ||
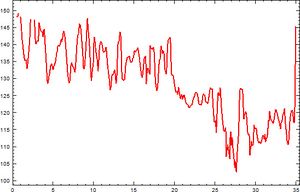
| − | Another use for the Relative Running Economy is to compare values within a run. [[Glycogen]] depletion will result in a drop in efficiency, and this can be seen in the efficiency value. The glycogen depletion causes more fat to be burned, and fat requires more oxygen to provide an equivalent amount of energy. The graph below shows my efficiency value during a long run, consisting of pacing a 3 hour marathon, then adding on 9 extra miles at a slower pace. You can see my efficiency value staying reasonably constant, with some variation for the hills, until about mile 19. From 19 to 26 you can see my efficiency value gradually dropping due to [[Glycogen]] depletion. After the marathon distance you can see some recovery as I refuel somewhat. | + | Another use for the Relative Running Economy is to compare values within a run. [[Glycogen]] depletion will result in a drop in efficiency, and this can be seen in the efficiency value. The glycogen depletion causes more fat to be burned, and fat requires more oxygen to provide an equivalent amount of energy. The graph below shows my efficiency value during a long run, consisting of pacing a 3-hour marathon, then adding on 9 extra miles at a slower pace. You can see my efficiency value staying reasonably constant, with some variation for the hills, until about mile 19. From 19 to 26 you can see my efficiency value gradually dropping due to [[Glycogen]] depletion. After the marathon distance you can see some recovery as I refuel somewhat. |
[[File:Efficiency and glycogen depeletion.jpg|none|thumb|300px|Efficiency value over a 35 mile run.]] | [[File:Efficiency and glycogen depeletion.jpg|none|thumb|300px|Efficiency value over a 35 mile run.]] | ||
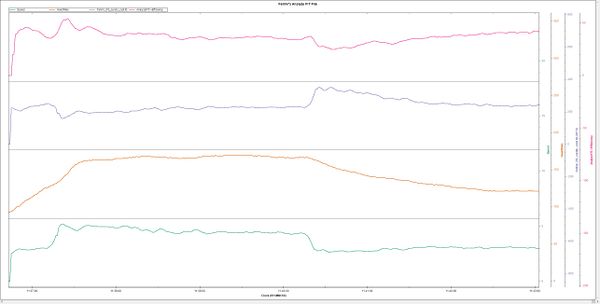
| + | =Billat's Cardiac Cost= | ||
| + | Veronique Billat produced a similar formula called "Cardiac Cost" in a research paper on marathon pacing<ref name="BillatPalacin2020"/>. The formula | ||
| + | Cardiac Cost = (Heart Rate / Speed) / 6000 | ||
| + | Where the speed is in meters per minute. Billat's formula uses [[Heart Rate]] on its own rather than adjusting for [[Resting Heart Rate]]. This formula is inverted, because it's looking at cost rather than efficiency. However, you can see the similarity below. (Note that Billat's paper shows the speed in both meters/minute and Km/minute. I queried this with Billat by email and confirmed this should be meters/second.) | ||
| + | [[File:RRE and CC.jpg|center|thumb|600px|Top to bottom: relative running economy, cardiac cost, heart rate, pace (form [[Stryd]].]] | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name="BillatPalacin2020">Véronique Louise Billat, Florent Palacin, Matthieu Correa, Jean-Renaud Pycke, Pacing Strategy Affects the Sub-Elite Marathoner's Cardiac Drift and Performance, Frontiers in Psychology, volume 10, 2020, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/1664-1078 1664-1078], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03026 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03026]</ref> | ||
<ref name="Saunders-2004"> PU. Saunders, DB. Pyne, RD. Telford, JA. Hawley, Factors affecting running economy in trained distance runners., Sports Med, volume 34, issue 7, pages 465-85, 2004, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15233599 15233599]</ref> | <ref name="Saunders-2004"> PU. Saunders, DB. Pyne, RD. Telford, JA. Hawley, Factors affecting running economy in trained distance runners., Sports Med, volume 34, issue 7, pages 465-85, 2004, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15233599 15233599]</ref> | ||
<ref name="Daniels-1985"> JT. Daniels, A physiologist's view of running economy., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 17, issue 3, pages 332-8, Jun 1985, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3894870 3894870]</ref> | <ref name="Daniels-1985"> JT. Daniels, A physiologist's view of running economy., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 17, issue 3, pages 332-8, Jun 1985, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3894870 3894870]</ref> | ||
<ref name="Jones2006">Andrew M. Jones, The Physiology of the World Record Holder for the Women's Marathon, International journal of Sports Science and Coaching, volume 1, issue 2, 2006, pages 101–116, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/1747-9541 1747-9541], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1260/174795406777641258 10.1260/174795406777641258]</ref> | <ref name="Jones2006">Andrew M. Jones, The Physiology of the World Record Holder for the Women's Marathon, International journal of Sports Science and Coaching, volume 1, issue 2, 2006, pages 101–116, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/1747-9541 1747-9541], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1260/174795406777641258 10.1260/174795406777641258]</ref> | ||
<ref name="Pereira-1997">MA. Pereira, PS. Freedson, Intraindividual variation of running economy in highly trained and moderately trained males., Int J Sports Med, volume 18, issue 2, pages 118-24, Feb 1997, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-972606 10.1055/s-2007-972606], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9081268 9081268]</ref> | <ref name="Pereira-1997">MA. Pereira, PS. Freedson, Intraindividual variation of running economy in highly trained and moderately trained males., Int J Sports Med, volume 18, issue 2, pages 118-24, Feb 1997, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-972606 10.1055/s-2007-972606], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9081268 9081268]</ref> | ||
| − | <references | + | </references> |
[[Category:Science]] | [[Category:Science]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:18, 5 May 2020
There are several components that make up running ability, including V̇O2max, and economy. V̇O2max is the ability of our bodies to generate energy for running and is the focus of a lot of our training. Running Economy is how far and fast you can run with a given amount of energy. Good economy is a critical part of running, and Cadence is one element I recommend runners focus on. (For the financial cost of running, see The Cost of Running.)
Contents
1 The Importance of Improving Running Economy
Running Economy can vary by as much as 30% between runners of a similar V̇O2max[1]. The two charts below show the V̇O2max and running economy of Paula Radcliffe over a 10-year period[2]. Over that time Paula Radcliffe's race performance dramatically improved even though her V̇O2max did not. This suggests that for elite athletes at least, improvements in running economy are critical.
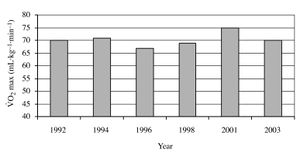 Paula Radcliffe's V̇O2max |
2 Improving Running Economy
There are several approaches that may improve your running economy. For details see The Science of Running Economy.
- Weight Loss. Losing weight can dramatically improve your running economy, as shown in my Running Calculator. (For those paying close attention, running economy is often normalized to the runner's weight, so that specific metric won't improve.)
- Cadence. The right Cadence is a key to efficient running and avoiding injury.
- Running Form. As well as Cadence, there are other aspects of Running Form that can improve running economy. For instance, step width can change running economy by 11%[3].
- High Intensity Interval Training. There are several studies that have shown that High Intensity Interval Training improves running economy.
- Heavy Weight Training and Plyometrics. Studies show these interventions can improve running economy by as 4-5%. Heavy weight training is 10 or less repetitions at 70% of 1 repetition maximum, using leg press, squats, etc. Plyometrics are explosive movements, such as Jumps. See Plyometrics for more details.
3 Measuring Running Economy
In an ideal world, we'd be able to easily measure our Running Economy and see if things are improving. If we could measure our breath, find out how much O2 we consumed and how much CO2 we produce, we'd know how much energy we burned (and from fat or carbohydrate). Such testing would require controlling the time of day, day of the week, diet, and footwear for each test[4] as well as specialist equipment that is not available to recreational runners. (Systems such as Cosmed's K5, PONE, and VO2 Master's VM Pro are becoming available, but cost thousands of dollars. Because this is not practical, the best measure we have of energy consumption is our Heart Rate. This is far from perfect, as Heart Rate can vary for other reasons besides supplying O2 for energy production. However, I believe it is a useful approximation and so I developed the simpler "Relative Running Economy." I've created an improved version called "HR-Pwr" which used the power estimate from Stryd to give a more useful estimate.
4 HrPwr Estimate of Running Economy
My initial approach was to use heart rate to estimate energy cost and distance covered to measure the effort. This works okay on the flat but is thrown off by changes in elevation. The Stryd footpod estimates the power output based on pace and elevation changes, which solves this problem nicely. It also gives the possibility of comparing data from running with cycling, though I've found the Stryd power estimate to be much higher for a given perceived effort than cycling. The formula I use is milliwatts per Kg per heartbeat, which I've called HrPwr (It's available as a Connect IQ data field.)
5 Relative Running Economy
This Relative Running Economy calculates a value based on how many heart beats are used for the distance covered. The formula that is shown below and there are more details at Relative Running Economy.
Total Beats = (Average Heart Rate – Resting Heart Rate) * Time in Minutes Work Per Mile = Total Beats / Distance in Miles Efficiency = 1 / Work Per Mile * 100,000
Note that the difference between Heart Rate and Resting Heart Rate is used to calculate the heart beats used for movement. Ideally the Heart Rate for standing would be used, but typically Resting Heart Rate is taken seated or lying down.
6 How to use Relative Running Economy
The calculated Relative Running Economy cannot easily be used to compare different runners. It can be used as to track how your running economy is improving over time, though it is also influenced by changes in fitness. Over the weeks and months of training your Relative Running Economy should gradually improve. For instance, I've seen my RRE go from 110-120 to 130-150 over a period of a few months. Sadly, I've also seen my RRE drop when I put on body fat (see Weight Loss and Performance.) This evaluation of my fitness this proved to be remarkably useful to me.
7 Relative Running Economy to detect Glycogen Depletion
Another use for the Relative Running Economy is to compare values within a run. Glycogen depletion will result in a drop in efficiency, and this can be seen in the efficiency value. The glycogen depletion causes more fat to be burned, and fat requires more oxygen to provide an equivalent amount of energy. The graph below shows my efficiency value during a long run, consisting of pacing a 3-hour marathon, then adding on 9 extra miles at a slower pace. You can see my efficiency value staying reasonably constant, with some variation for the hills, until about mile 19. From 19 to 26 you can see my efficiency value gradually dropping due to Glycogen depletion. After the marathon distance you can see some recovery as I refuel somewhat.
8 Billat's Cardiac Cost
Veronique Billat produced a similar formula called "Cardiac Cost" in a research paper on marathon pacing[5]. The formula
Cardiac Cost = (Heart Rate / Speed) / 6000
Where the speed is in meters per minute. Billat's formula uses Heart Rate on its own rather than adjusting for Resting Heart Rate. This formula is inverted, because it's looking at cost rather than efficiency. However, you can see the similarity below. (Note that Billat's paper shows the speed in both meters/minute and Km/minute. I queried this with Billat by email and confirmed this should be meters/second.)
9 References
- ↑ JT. Daniels, A physiologist's view of running economy., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 17, issue 3, pages 332-8, Jun 1985, PMID 3894870
- ↑ Andrew M. Jones, The Physiology of the World Record Holder for the Women's Marathon, International journal of Sports Science and Coaching, volume 1, issue 2, 2006, pages 101–116, ISSN 1747-9541, doi 10.1260/174795406777641258
- ↑ PU. Saunders, DB. Pyne, RD. Telford, JA. Hawley, Factors affecting running economy in trained distance runners., Sports Med, volume 34, issue 7, pages 465-85, 2004, PMID 15233599
- ↑ MA. Pereira, PS. Freedson, Intraindividual variation of running economy in highly trained and moderately trained males., Int J Sports Med, volume 18, issue 2, pages 118-24, Feb 1997, doi 10.1055/s-2007-972606, PMID 9081268
- ↑ Véronique Louise Billat, Florent Palacin, Matthieu Correa, Jean-Renaud Pycke, Pacing Strategy Affects the Sub-Elite Marathoner's Cardiac Drift and Performance, Frontiers in Psychology, volume 10, 2020, ISSN 1664-1078, doi 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03026