User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]] is the difference between [[Resting Heart Rate]] taken when lying down and [[Heart Rate]] when standing. The test measures how the heart responds to the added stress of standing up, which requires the heart to pump against gravity. The Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]] is sometimes considered a [[Overtraining Syndrome Symptoms|Symptom of Overtraining Syndrome]].
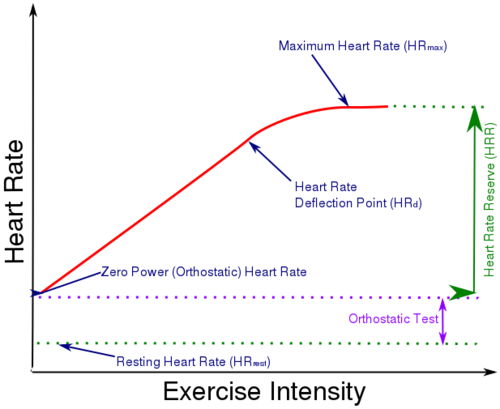
| + | [[File:HeartRateSimplified.svg|right|thumb|500px|A simplified chart of heart rate against exercise intensity showing [[Maximum Heart Rate]], [[Heart Rate Reserve]], [[Resting Heart Rate]], [[Orthostatic Heart Rate]], and [[Heart Rate Deflection]].]] |
| − | | + | The Orthostatic Heart Rate the heart rate when standing. This [[Heart Rate]] is slightly above [[Resting Heart Rate]] as resting HR is taken either lying down or seated. A difference between Resting Heart Rate and Orthostatic Heart Rate is normally 10-15 BPM. I believe this is a more useful value than resting heart rate as it reflects the Heart Rate a "zero power". The Orthostatic Heart Rate is part of the [[Orthostatic Heart Rate Test]]. |
| − | =Performing the Orthostatic Heart Rate Test=
| |
| − | There are wide variations<ref name="OhInconst"/> in the details of how to perform this test, so the following is based on a research study that compared different approaches to determine the optimal solution<ref name="OhComp"/>.
| |
| − | * For monitoring [[Overtraining Syndrome]], the test should be performed in the same way and under the same conditions each day.
| |
| − | * This test is normally performed on waking in the morning. If performed at other times, avoid things that change [[Heart Rate]] such as exercise, stress or [[Caffeine]] before the test.
| |
| − | * Taking the [[Heart Rate]] reading should be done in such a way that it requires no effort on the part of the subject. A [[Heart Rate Monitor]] is ideal, and a [[Pulse Oximeter]] works well.
| |
| − | * The [[Resting Heart Rate]] should be taken after lying down for at least 5 minutes, preferably 10 minutes<ref name="OhComp"/>. Lying down for longer is not required, but it is also not a problem.
| |
| − | * Stand up gently and remain still for 2 minutes before taking a second [[Heart Rate]] reading<ref name="OhComp"/>.
| |
| − | * The difference between the two readings is the Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | =What does the Orthostatic Heart Rate Test detect?=
| |
| − | A high Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]] has been suggested as a symptom of [[Overtraining Syndrome]], but it can also be caused by a viral infection, diabetes mellitus, as well as autoimmune and neurodegenerative disorders <ref name="OhRef"/>. There seems to be little evidence to support the Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]] Test as a reliable method of predicting or detecting [[Overtraining Syndrome]]. However, this test is generally easy to perform and may be useful when considered as one possible indicator that can be factored in.
| |
| − | | |
| − | =What does the number mean?=
| |
| − | An Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]] rise of 30 BPM or more is a sign of Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (see below) and would indicate that a medical evaluation is appropriate. For detecting [[Overtraining Syndrome]] it is an increase in the size of the rise, based on an established baseline. That makes it tough to use this test for suspected [[Overtraining Syndrome]] unless there is a history of measurement that can be used for comparison. It has been suggested that an Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]] rise of 10-15 BPM is considered 'normal', and an increase of 5 BPM over baseline is indicative of [[Overtraining Syndrome]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | =Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome=
| |
| − | Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is the Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]] is more than a 30 BPM rise, or the standing [[Heart Rate]] is greater than 120 BPM<ref name="Pots"/>. People with POTS have problems with lightheadedness or fainting when standing up.
| |
| − | | |
| − | =Polar OwnOptimizer=
| |
| − | Some Polar [[Heart Rate Monitors]] include a version of the Orthostatic [[Heart Rate]] called OwnOptimizer<ref name="PolarOwn"/>. This test uses other [[Heart Rate]] parameters, such as [[Heart Rate Variability]] to indicate [[Overtraining Syndrome]]. There is some limited scientific evidence that the Polar test can detect intense training<ref name="PolarOTScience"/>, but there is no evidence that is predicts or detects [[Overtraining Syndrome]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | =References=
| |
| − | <references>
| |
| − | <ref name="PolarOTScience"> http://www.polar.fi/en/about_polar/who_we_are/research/overtraining_test </ref>
| |
| − | <ref name="Pots">Postural Tachycardia Syndrome Information Page: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/postural_tachycardia_syndrome/postural_tachycardia_syndrome.htm </ref>
| |
| − | <ref name="OhInconst">Medscape Log In http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/474822_2 </ref>
| |
| − | <ref name="OhComp">Comparison of different methods of obtaining o... [Clin Nurs Res. 2000] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11881701 </ref>
| |
| − | <ref name="OhRef">Orthostatic heart rate and blood pressure in ... [J Child Neurol. 2010] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20197269 </ref>
| |
| − | <ref name="PolarOwn"> http://www.polarusa.com/us-en/support/OwnOptimizer?product_id=7881&category=tips </ref>
| |
| − | </references>
| |