Difference between revisions of "Foot Strike"
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
While Strike Index is a good measure of Foot Strike, it requires sophisticated equipment to measure the pressure the foot makes as it lands. A simpler approach is to look at the angle of the foot as it touches down, called Foot Strike Angle (FSA). It is practical to evaluate FSA with [[High Speed Video Analysis]]. A study compared the two approaches and found there was a good correlation between Strike Index and FSA<ref name="AltmanDavis2012"/>. Note in the graph below the wide range of strike indexes for RFS, from nearly 0 (the extreme back of the heel) to close to the 33% mark, which is well in front of the heel bone. | While Strike Index is a good measure of Foot Strike, it requires sophisticated equipment to measure the pressure the foot makes as it lands. A simpler approach is to look at the angle of the foot as it touches down, called Foot Strike Angle (FSA). It is practical to evaluate FSA with [[High Speed Video Analysis]]. A study compared the two approaches and found there was a good correlation between Strike Index and FSA<ref name="AltmanDavis2012"/>. Note in the graph below the wide range of strike indexes for RFS, from nearly 0 (the extreme back of the heel) to close to the 33% mark, which is well in front of the heel bone. | ||
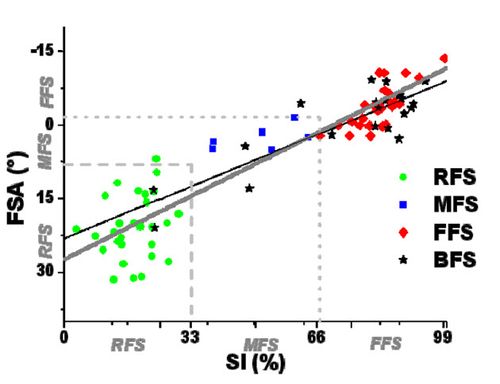
[[File:Foot Strike Angle.jpg|none|thumb|500px|A graph of Foot Strikes, with each point showing Strike Index against Foot Strike Angle<ref name="AltmanDavis2012"/>. A Foot Strike Angle of 0 degrees means the foot is level with the ground on first contact. The color coding indicates the visual categorization of the Foot Strike.]] | [[File:Foot Strike Angle.jpg|none|thumb|500px|A graph of Foot Strikes, with each point showing Strike Index against Foot Strike Angle<ref name="AltmanDavis2012"/>. A Foot Strike Angle of 0 degrees means the foot is level with the ground on first contact. The color coding indicates the visual categorization of the Foot Strike.]] | ||
| − | = | + | =Evaluating Your Foot Strike= |
| − | [[RunScribe]] | + | It seems intuitively obvious that a runner will know how their foot lands. However, it seems that runners are actually relatively poor at evaluating their foot strike. A study of 60 runners found that only 70% knew their foot strike<ref name="GossLewek2015"/>, while another study found that only 44% of recreational runners and 57% of collegiate cross-country runners knew their foot strike<ref name="Bade-2016"/>. This is in line with a study of 87 runners that showed only 69% were correct in their identification of their foot strike<ref name="Goss-2012"/>. Personally, I suspect that the extremes of foot strike are relatively easy to distinguish. A forefoot runner whose heel never touches the ground is pretty obviously a forefoot runner. Likewise, many runners are quite obviously extreme heel strikers. Between those extremes that becomes far more uncertainty, and a more objective measure becomes valuable. The two options I'm aware of for evaluating foot strike are high-speed video and the [[RunScribe]] Footpod. High speed video can be quite effective, and the cameras are becoming far more accessible, but it still can be rather tricky to evaluate. I found the [[RunScribe]] Footpod to be the easiest option, and it provides many other metrics. |
=Foot Strike science= | =Foot Strike science= | ||
The optimum Foot Strike is unclear given the available evidence. | The optimum Foot Strike is unclear given the available evidence. | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name="GossLewek2015">Donald L. Goss, Michael Lewek, Bing Yu, William B. Ware, Deydre S. Teyhen, Michael T. Gross, Lower Extremity Biomechanics and Self-Reported Foot-Strike Patterns Among Runners in Traditional and Minimalist Shoes, Journal of Athletic Training, volume 50, issue 6, 2015, pages 603–611, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/1062-6050 1062-6050], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050.49.6.06 10.4085/1062-6050.49.6.06]</ref> | ||
<ref name="NiggBahlsen1987">B.M. Nigg, H.A. Bahlsen, S.M. Luethi, S. Stokes, The influence of running velocity and midsole hardness on external impact forces in heel-toe running, Journal of Biomechanics, volume 20, issue 10, 1987, pages 951–959, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/00219290 00219290], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0021-9290(87)90324-1 10.1016/0021-9290(87)90324-1]</ref> | <ref name="NiggBahlsen1987">B.M. Nigg, H.A. Bahlsen, S.M. Luethi, S. Stokes, The influence of running velocity and midsole hardness on external impact forces in heel-toe running, Journal of Biomechanics, volume 20, issue 10, 1987, pages 951–959, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/00219290 00219290], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0021-9290(87)90324-1 10.1016/0021-9290(87)90324-1]</ref> | ||
<ref name="KellerWeisberger1996">TS Keller, AM Weisberger, JL Ray, SS Hasan, RG Shiavi, DM Spengler, Relationship between vertical ground reaction force and speed during walking, slow jogging, and running, Clinical Biomechanics, volume 11, issue 5, 1996, pages 253–259, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/02680033 02680033], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0268-0033(95)00068-2 10.1016/0268-0033(95)00068-2]</ref> | <ref name="KellerWeisberger1996">TS Keller, AM Weisberger, JL Ray, SS Hasan, RG Shiavi, DM Spengler, Relationship between vertical ground reaction force and speed during walking, slow jogging, and running, Clinical Biomechanics, volume 11, issue 5, 1996, pages 253–259, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/02680033 02680033], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0268-0033(95)00068-2 10.1016/0268-0033(95)00068-2]</ref> | ||
| Line 84: | Line 85: | ||
<ref name="KasmerLiu2013">Mark E. Kasmer, Xue-cheng Liu, Kyle G. Roberts, Jason M. Valadao, The relationship of foot strike pattern, shoe type, and performance in a 50-km trail race, Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2013, pages 1, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/1064-8011 1064-8011], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182a20ed4 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182a20ed4]</ref> | <ref name="KasmerLiu2013">Mark E. Kasmer, Xue-cheng Liu, Kyle G. Roberts, Jason M. Valadao, The relationship of foot strike pattern, shoe type, and performance in a 50-km trail race, Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2013, pages 1, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/1064-8011 1064-8011], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182a20ed4 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182a20ed4]</ref> | ||
<ref name="Kasmer-2014">ME. Kasmer, JJ. Wren, MD. Hoffman, Foot strike pattern and gait changes during a 161-km ultramarathon., J Strength Cond Res, volume 28, issue 5, pages 1343-50, May 2014, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000000282 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000282], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24149763 24149763]</ref> | <ref name="Kasmer-2014">ME. Kasmer, JJ. Wren, MD. Hoffman, Foot strike pattern and gait changes during a 161-km ultramarathon., J Strength Cond Res, volume 28, issue 5, pages 1343-50, May 2014, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000000282 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000282], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24149763 24149763]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Bade-2016">MB. Bade, K. Aaron, TG. McPoil, ACCURACY OF SELF-REPORTED FOOT STRIKE PATTERN IN INTERCOLLEGIATE AND RECREATIONAL RUNNERS DURING SHOD RUNNING., Int J Sports Phys Ther, volume 11, issue 3, pages 350-5, Jun 2016, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27274421 27274421]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Goss-2012">DL. Goss, MT. Gross, Relationships among self-reported shoe type, footstrike pattern, and injury incidence., US Army Med Dep J, pages 25-30, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23007933 23007933]</ref> | ||
</references> | </references> | ||
Revision as of 09:40, 22 June 2016
Foot Strike is the way the foot lands while running, and the best Foot Strike pattern is both controversial and unclear. It seems likely that other factors beyond the simplistic classifications of forefoot, midfoot or rear Foot Strike are important, especially Cadence and Overstriding. My suggestion is to focus on optimizing Cadence and reducing Overstriding rather than directly trying to change your Foot Strike pattern.
Contents
1 Foot Strike classifications
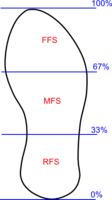
While running, the way the foot lands is often classified as Fore Foot Strike (FFS), Mid Foot Strike (MFS) or Rear Foot Strike (RFS), though there is variation in these definitions[1].
- In FFS, the forefoot lands first and can either be followed by the heel landing later or by the heel remaining above the ground.
- Generally MFS has the outside edge of the middle of the foot landing first, but some definitions include the locations from just in front of the heel to just behind the forefoot. After this edge lands, the foot flattens and both forefoot and heel are in contact with the ground.
- RFS is where the heel of the foot lands first, followed by the forefoot. This pattern can vary from a landing on the extreme back of the heel with the forefoot elevated through to a nearly MFS landing where the heel touches down just before the forefoot. In some cases the bulk of the landing forces are absorbed by the heel, where in other cases the bulk of the landing force is absorbed by the forefoot. RFS is often termed Heel Strike.
There is also a suggestion that the point of maximum loading should be used to determine foot strike instead of the initial contact point. This is because some runners may make only light contact with the heel, sometimes referred to as "proprioceptive heel strike".
1.1 Strike Index
A more precise approach to Foot Strike is to measure the position of the center of pressure of the initial contact of the foot[2]. This strike index is then this position as a percentage of the length of the foot.
- Strike Index
1.2 Foot Strike angle
While Strike Index is a good measure of Foot Strike, it requires sophisticated equipment to measure the pressure the foot makes as it lands. A simpler approach is to look at the angle of the foot as it touches down, called Foot Strike Angle (FSA). It is practical to evaluate FSA with High Speed Video Analysis. A study compared the two approaches and found there was a good correlation between Strike Index and FSA[2]. Note in the graph below the wide range of strike indexes for RFS, from nearly 0 (the extreme back of the heel) to close to the 33% mark, which is well in front of the heel bone.
2 Evaluating Your Foot Strike
It seems intuitively obvious that a runner will know how their foot lands. However, it seems that runners are actually relatively poor at evaluating their foot strike. A study of 60 runners found that only 70% knew their foot strike[3], while another study found that only 44% of recreational runners and 57% of collegiate cross-country runners knew their foot strike[4]. This is in line with a study of 87 runners that showed only 69% were correct in their identification of their foot strike[5]. Personally, I suspect that the extremes of foot strike are relatively easy to distinguish. A forefoot runner whose heel never touches the ground is pretty obviously a forefoot runner. Likewise, many runners are quite obviously extreme heel strikers. Between those extremes that becomes far more uncertainty, and a more objective measure becomes valuable. The two options I'm aware of for evaluating foot strike are high-speed video and the RunScribe Footpod. High speed video can be quite effective, and the cameras are becoming far more accessible, but it still can be rather tricky to evaluate. I found the RunScribe Footpod to be the easiest option, and it provides many other metrics.
3 Foot Strike science
The optimum Foot Strike is unclear given the available evidence.
- While runners can be categorized as RFS, MFS, FFS, in practice runners vary along a spectrum[6].
- Two studies showed no difference in Running Economy between FFS and RFS[7][8].
- A study compared the Running Economy of habitually FFS and RFS runners when running both FFS and RFS[9]. The runners were relatively fast, with a typical training pace of 7:15 min/mile and running 28 miles/week. The FFS group actually consisted of both FFS and MFS runners, and there were 14 MFS and only 4 FFS runners in the FFS group, with 19 in the RFS group. Each group was tested at slow (9:00 min/mile), medium (7:40 min/mile) and fast (6:45 min/mile) paces with both FFS and RFS. The results were:
- Using their habitual foot strike the FFS were very slightly more efficient at medium and fast speeds, but this was not statistically significant. (Estimating from the graphs, this is ~1 mg/kg/min.)
- At the slow and medium speed the FFS group using either FFS or RFS and the RFS group running RFS used the same oxygen, but the RFS group running FFS was less efficient. (So if you're a RFS runner, you're likely to be less efficient when running FFS until you get used to it, at which point you'll be back to your prior efficiency.)
- At the fast speed both groups were less efficient with a FFS.
- In nearly all situations a RFS used less a lower percentage of carbohydrate than a FFS, the only exception being the FFS group at slow speeds. (This was only statistically significant at the slow speed.)
- Runners tend to shift from RFS to MFS or FFS as they run faster, with runners becoming predominantly FFS at faster than 4:30 min/mile and predominantly RFS as 5:15 min/mile or slower[10][11].
- One study found that habitually barefoot endurance runners are predominantly FFS, with some MFS but fewer RFS, though the pace evaluated was quite fast (5:15-4:30 min/mile)[12]. Another study showed that at endurance running speeds, habitually barefoot runners were 83% RFS, 17% MFS and none were FFS[13]. At faster speeds, this changed, and at around 5 min/mile pace there were 43% RFS, 43% MFS and 14% FFS, then above 4 min/mile the breakdown changed again to 40% RFS, 60% MFS, and no FFS[13].
- A study trained 20 runners in the pose method that uses a FFS along with other modifications to the Running Form including a higher Cadence[14]. The pose method resulted is less vertical movement, which may be the result of the FFS, the higher cadence, or both. The pose method reduced the eccentric load on the knee, but increased it in the ankle compared with MFS and RFS. This suggests that the pose method may help reduce the stress on the knee, but at the cost of additional stress on the calf and Achilles tendon.
- The evaluation of 52 competitive middle and long distance collegiate athletes found that RFS runners were 2.6 times more likely to have a mild repetitive strain injury and 2.4 times more likely to have a moderate repetitive strain injury than FFS[1].
- The RFS runners had 2-4x the injury rate for injuries that would be expected to come from a RFS than FFS runners. These injuries were hip pain, Knee Pain, lower back pain, tibial stress injuries, Plantar Fasciitis, and stress fractures of lower limb bones excluding the metatarsal.
- The injuries that were expected to be related to FFS were not actually different between FFS and RFS. These injuries were Achilles tendinopathies, foot pain, and metatarsal stress fractures.
- Note that the sample size was small, and some FFS runners had high injury rates while some RFS runners had low injury rates. The overall injury rate was high, with 75% of runners having at least one moderate or severe repetitive stress injury per year. This high injury rate is probably due to the competitive nature of collegiate sports.
- Analysis of 240 female RFS runners found that runners were injured over a two year period had higher impact forces than those that were not injured[15]. No analysis of other Foot Strike patterns was performed.
- Most[12][14][6], but not all[16] studies show that RFS have higher impact forces than FFS. Note that impact force tends to increase with pace[13][10], and impact is reduced with a higher Cadence[17][18][19].
- One study found that some runners made initial contact with the heal (RFS), but it was midfoot when the foot became loaded[20]. About a quarter of runners that made initial contact at the rear had the maximum loading occur midfoot. This raises a question around the classification of foot strike; should we consider the initial contact point or the point of maximum loading?
- There have been a few studies looking at foot strike patterns in races. This research does not indicate the optimal Foot Strike, but it gives some idea of prevalence.
- The Foot Strike patterns of 415 runners were evaluated at an elite half marathon in Japan, and 74.9% were RFS, 23.7% were MFS and 1.4% were FFS[21]. For the fastest 50 runners the Foot Strikes were 62.0% RFS, 36.0% MFS, and 2.0% FFS.
- Analysis of 286 runners at the 10K point of the 2009 Manchester (US) marathon showed 87.8% were RFS, 3.1% MFS, and 1.4% FFS (7.7% were asymmetric)[22]. At the 32K point the mixture had changed, with more RFS (93%) and midfoot (3.5%). No runners were FFS at the 32K point, though 3.5% were asymmetric. This study showed no relationship between pace and foot strike, but the runners in this race did not have the faster elite runners.
- A study of 1991 runners at 8Km mark of the 2011 Milwaukee Marathon showed that 93.7% were RFS, but faster runners were more likely to be FFS[23].
- In a 50K trail race 85% were RFS at the 8KM point[24].
- RFS Runners in a 100 mile trail race made up 80% @ 16K, 89% @ 90K, and 84% @ finish[25]. The non-RFS runners had more muscle damage (CK levels) than RFS runners at the latter two stages.
- There is almost no research into the effect of changing Foot Strike patterns. There is a report of two runners that had stress fractures in their foot after changing from RFS to MFS, but they also changed to FiveFingers as well[26] .
- I found no studies that looked at strike pattern and cadence to evaluate the interactions between these two factors. It seems possible to me that RFS is more common with runners who have a lower cadence, and that many of the negative implications of RFS are actually due to a low cadence. However, this is pure supposition at this point.
4 Limitations of the available science
There are a number of limitations to the available science that should be noted.
- The classification of Foot Strike into FFS, MFS and RFS seems overly simplistic. I believe that FFS in particular should be subdivided into those strike patterns where the forefoot lands first, followed by the heel and those where the heel never touches down. I also believe that where the heel is in contact with the ground at some point, Foot Strike should be considered a continuum of values based on Strike Index, rather than as discrete groupings.
- Foot Strike should be considered in conjunction with the possible confounding variables of cadence and overstriding. It would be useful to know where any correlation is linked to each of the three variables.
5 Recommendations
While there is not sufficient evidence to make any clear recommendations around Foot Strike, I would suggest the following:
- There is no clear evidence that one strike pattern is better than another, but MFS and FFS seem to have lower impact and injury risk than RFS. However, there is a wide variation in impact and injury rates within RFS, so other factors such as Cadence or Overstriding may be the underlying cause.
- Be cautious in changing your Foot Strike pattern, as there is anecdotal evidence of injury associated with the change.
- For RFS runners, increasing Cadence and reducing Overstriding may move the strike further forward without requiring a complete change in Running Form.
- If you are having calf or ankle problems and you are a FFS runner who does not touch down with your heel, consider a change so that your weight is taken by your heel at some point during the stance phase of running.
- For new runners, I would suggest doing what comes naturally.
- Listen to the sound your feet make as they land, as this can give an indication of biomechanical problems.
6 References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 AI. Daoud, GJ. Geissler, F. Wang, J. Saretsky, YA. Daoud, DE. Lieberman, Foot Strike and injury rates in endurance runners: a retrospective study., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 44, issue 7, pages 1325-34, Jul 2012, doi 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3182465115, PMID 22217561
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Allison R. Altman, Irene S. Davis, A kinematic method for footstrike pattern detection in barefoot and shod runners, Gait & Posture, volume 35, issue 2, 2012, pages 298–300, ISSN 09666362, doi 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2011.09.104
- ↑ Donald L. Goss, Michael Lewek, Bing Yu, William B. Ware, Deydre S. Teyhen, Michael T. Gross, Lower Extremity Biomechanics and Self-Reported Foot-Strike Patterns Among Runners in Traditional and Minimalist Shoes, Journal of Athletic Training, volume 50, issue 6, 2015, pages 603–611, ISSN 1062-6050, doi 10.4085/1062-6050.49.6.06
- ↑ MB. Bade, K. Aaron, TG. McPoil, ACCURACY OF SELF-REPORTED FOOT STRIKE PATTERN IN INTERCOLLEGIATE AND RECREATIONAL RUNNERS DURING SHOD RUNNING., Int J Sports Phys Ther, volume 11, issue 3, pages 350-5, Jun 2016, PMID 27274421
- ↑ DL. Goss, MT. Gross, Relationships among self-reported shoe type, footstrike pattern, and injury incidence., US Army Med Dep J, pages 25-30, PMID 23007933
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 PR. Cavanagh, MA. Lafortune, Ground reaction forces in distance running., J Biomech, volume 13, issue 5, pages 397-406, 1980, PMID 7400169
- ↑ DP. Perl, AI. Daoud, DE. Lieberman, Effects of footwear and strike type on running economy., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 44, issue 7, pages 1335-43, Jul 2012, doi 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318247989e, PMID 22217565
- ↑ CB. Cunningham, N. Schilling, C. Anders, DR. Carrier, The influence of foot posture on the cost of transport in humans., J Exp Biol, volume 213, issue 5, pages 790-7, Mar 2010, doi 10.1242/jeb.038984, PMID 20154195
- ↑ AH. Gruber, BR. Umberger, B. Braun, J. Hamill, Economy and rate of carbohydrate oxidation during running with rearfoot and foreFoot Strike patterns., J Appl Physiol, May 2013, doi 10.1152/japplphysiol.01437.2012, PMID 23681915
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 TS Keller, AM Weisberger, JL Ray, SS Hasan, RG Shiavi, DM Spengler, Relationship between vertical ground reaction force and speed during walking, slow jogging, and running, Clinical Biomechanics, volume 11, issue 5, 1996, pages 253–259, ISSN 02680033, doi 10.1016/0268-0033(95)00068-2
- ↑ B.M. Nigg, H.A. Bahlsen, S.M. Luethi, S. Stokes, The influence of running velocity and midsole hardness on external impact forces in heel-toe running, Journal of Biomechanics, volume 20, issue 10, 1987, pages 951–959, ISSN 00219290, doi 10.1016/0021-9290(87)90324-1
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Daniel E. Lieberman, Madhusudhan Venkadesan, William A. Werbel, Adam I. Daoud, Susan D'Andrea, Irene S. Davis, Robert Ojiambo Mang'Eni, Yannis Pitsiladis, Foot Strike patterns and collision forces in habitually barefoot versus shod runners, Nature, volume 463, issue 7280, 2010, pages 531–535, ISSN 0028-0836, doi 10.1038/nature08723
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Alejandro Lucia, Kevin G. Hatala, Heather L. Dingwall, Roshna E. Wunderlich, Brian G. Richmond, Variation in Foot Strike Patterns during Running among Habitually Barefoot Populations, PLoS ONE, volume 8, issue 1, 2013, pages e52548, ISSN 1932-6203, doi 10.1371/journal.pone.0052548
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 RE. Arendse, TD. Noakes, LB. Azevedo, N. Romanov, MP. Schwellnus, G. Fletcher, Reduced eccentric loading of the knee with the pose running method., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 36, issue 2, pages 272-7, Feb 2004, doi 10.1249/01.MSS.0000113684.61351.B0, PMID 14767250
- ↑ Do impacts cause running injuries? A prospective investigation, Irene S. Davis, Bradley Bowser and David Mullineaux. American Society of Biomechanics, 2010 conference abstract
- ↑ Laughton, Carrie A., I. M. Davis, and Joseph Hamill. "Effect of strike pattern and orthotic intervention on tibial shock during running." Journal of Applied Biomechanics 19.2 (2003): 153-168.
- ↑ BC. Heiderscheit, ES. Chumanov, MP. Michalski, CM. Wille, MB. Ryan, Effects of step rate manipulation on joint mechanics during running., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 43, issue 2, pages 296-302, Feb 2011, doi 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181ebedf4, PMID 20581720
- ↑ JA. Mercer, P. Devita, TR. Derrick, BT. Bates, Individual effects of stride length and frequency on shock attenuation during running., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 35, issue 2, pages 307-13, Feb 2003, doi 10.1249/01.MSS.0000048837.81430.E7, PMID 12569221
- ↑ Hamill, J., T. R. Derrick, and K. G. Holt. "Shock attenuation and stride frequency during running." Human Movement Science 14.1 (1995): 45-60.
- ↑ Bastiaan Breine, Philippe Malcolm, Edward C. Frederick, Dirk DeClercq, Initial foot contact patterns during steady state shod running, Footwear Science, volume 5, issue sup1, 2013, pages S81–S82, ISSN 1942-4280, doi 10.1080/19424280.2013.799570
- ↑ H. Hasegawa, T. Yamauchi, WJ. Kraemer, Foot Strike patterns of runners at the 15-km point during an elite-level half marathon., J Strength Cond Res, volume 21, issue 3, pages 888-93, Aug 2007, doi 10.1519/R-22096.1, PMID 17685722
- ↑ Peter Larson, Erin Higgins, Justin Kaminski, Tamara Decker, Janine Preble, Daniela Lyons, Kevin McIntyre, Adam Normile, Foot strike patterns of recreational and sub-elite runners in a long-distance road race, Journal of Sports Sciences, volume 29, issue 15, 2011, pages 1665–1673, ISSN 0264-0414, doi 10.1080/02640414.2011.610347
- ↑ ME. Kasmer, XC. Liu, KG. Roberts, JM. Valadao, Foot-strike pattern and performance in a marathon., Int J Sports Physiol Perform, volume 8, issue 3, pages 286-92, May 2013, PMID 23006790
- ↑ Mark E. Kasmer, Xue-cheng Liu, Kyle G. Roberts, Jason M. Valadao, The relationship of foot strike pattern, shoe type, and performance in a 50-km trail race, Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 2013, pages 1, ISSN 1064-8011, doi 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182a20ed4
- ↑ ME. Kasmer, JJ. Wren, MD. Hoffman, Foot strike pattern and gait changes during a 161-km ultramarathon., J Strength Cond Res, volume 28, issue 5, pages 1343-50, May 2014, doi 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000282, PMID 24149763
- ↑ J. Giuliani, B. Masini, C. Alitz, BD. Owens, Barefoot-simulating footwear associated with metatarsal stress injury in 2 runners., Orthopedics, volume 34, issue 7, pages e320-3, Jul 2011, doi 10.3928/01477447-20110526-25, PMID 21717998