Difference between revisions of "CoolSculpting"
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) (Created page with "It seems like everyone wants to be leaner. Losing body fat is big business and one of the latest approaches is CoolSculpting ®, also...") |
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
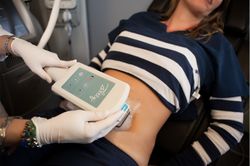
[[File:CoolSculpting device.jpg|right|thumb|250px|The CoolSculpting device.]] | [[File:CoolSculpting device.jpg|right|thumb|250px|The CoolSculpting device.]] | ||
The device removes heat from the skin at a constant rate, rather than chilling to a particular temperature. While the underlying mechanism is unclear<ref name="ClNelson"/>, the current theory is that chilling fat tissues to just below freezing triggers inflammation of the fat cells ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Panniculitis Panniculitis]) and then triggers natural cell death in the fat cells ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosis apoptosis]). The inflammation starts 3 days after treatment, peaking at 30 days, with some residual inflammation seen after 90 days and the number of fat cells declining over the 90 day period<ref name="CsPig"/>. | The device removes heat from the skin at a constant rate, rather than chilling to a particular temperature. While the underlying mechanism is unclear<ref name="ClNelson"/>, the current theory is that chilling fat tissues to just below freezing triggers inflammation of the fat cells ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Panniculitis Panniculitis]) and then triggers natural cell death in the fat cells ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosis apoptosis]). The inflammation starts 3 days after treatment, peaking at 30 days, with some residual inflammation seen after 90 days and the number of fat cells declining over the 90 day period<ref name="CsPig"/>. | ||
| − | =CoolSculpting | + | =What about frostbite?= |
| − | Cryosurgery uses cold to kill off tissue, such as tumors. Typically cryosurgery uses far lower temperatures (-20c/-4f to -40c/-40f) and kills off the living cells ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Necrosis necrosis]) <ref name="CryosurgeryTemp"/>. | + | A common concern is frostbite, or other damage to the skin. This is not a problem, as you need far colder temperatures to cause that type of damage. CoolSculpting uses temperatures that do not immediately kill off the fat cells, but rather trigger the natural process of cell death([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosis apoptosis]). That's why CoolSculpting takes weeks or months for the full effect to be seen. |
| + | =CoolScuplting compared with Cryosurgery= | ||
| + | CoolScuplting is quite different to Cryosurgery, which uses cold to kill off tissue, such as tumors. Typically cryosurgery uses far lower temperatures (-20c/-4f to -40c/-40f) and immediately kills off the living cells ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Necrosis necrosis]) <ref name="CryosurgeryTemp"/>. Cell damage is caused by temperatures below -10c/14f and CoolSculpting only drops the temperature to around -1c/31f. | ||
=Side effects of CoolSculpting= | =Side effects of CoolSculpting= | ||
There have been no serious side effects reported so far<ref name="ClNelson"/>. The skin being treated goes red, with some bruising and numbness. I suspect that the bruising may be because the CoolSculpting device sucks<ref name="CsSuction"/><ref name="CryroNerves"/> the fat against the cooling device. These problems normally resolve within a week. Studies have shown no changes in blood lipid levels or liver function<ref name="CyroMeta"/>. The numbness is not associated with nerve damage<ref name="CryroNerves"/>. | There have been no serious side effects reported so far<ref name="ClNelson"/>. The skin being treated goes red, with some bruising and numbness. I suspect that the bruising may be because the CoolSculpting device sucks<ref name="CsSuction"/><ref name="CryroNerves"/> the fat against the cooling device. These problems normally resolve within a week. Studies have shown no changes in blood lipid levels or liver function<ref name="CyroMeta"/>. The numbness is not associated with nerve damage<ref name="CryroNerves"/>. | ||
| − | =Spot Reduction | + | =Weight Loss or Spot Reduction?= |
| − | CoolSculpting reduces the fat thickness in the limited area that is treated rather than producing overall weight loss<ref name="ClNelson"/>. CoolSculpting does not seem to be effective in obese people, though it may simply be harder to observe the effects<ref name="ClNelson"/>. | + | CoolSculpting reduces the fat thickness in the limited area that is treated rather than producing overall weight loss<ref name="ClNelson"/>. CoolSculpting does not seem to be effective in obese people, though it may simply be harder to observe the effects<ref name="ClNelson"/>. It's worth noting that CoolSculpting reduces the fat thickness in people who have a stable weight; in other words, you don't need to be on a diet for it to work. |
| + | =How long does it take to work?= | ||
| + | The effects of CoolSculpting should start within a few weeks, but the full effect may take 3-4 months<ref name="CsPig"/>. | ||
=DIY CoolSculpting= | =DIY CoolSculpting= | ||
Having reviewed the evidence for the commercial CoolSculpting, I wondered if it would be possible to replicate the effects by simply applying ice to the skin. The levels of fat on my legs are noticeably lower than other parts of my body, which might be the result of regular icing. There is evidence that applying ice to the skin produces an inflammation response in just a few minutes<ref name="CyroMeta"/>, so this approach seems viable. | Having reviewed the evidence for the commercial CoolSculpting, I wondered if it would be possible to replicate the effects by simply applying ice to the skin. The levels of fat on my legs are noticeably lower than other parts of my body, which might be the result of regular icing. There is evidence that applying ice to the skin produces an inflammation response in just a few minutes<ref name="CyroMeta"/>, so this approach seems viable. | ||
Revision as of 06:31, 12 May 2012
Losing body fat is big business and one of the latest approaches is CoolSculpting ®, also called Cryolipolysis®. The word 'Cryolipolysis' literally means "cold fat loss", and CoolSculpting works by chilling the skin so that the underlying fat cells are reduced. I've found that a similar effect can be produced at home for almost no cost.
Contents
[hide]1 CoolSculpting
CoolSculpting uses an FDA approved device to chill the skin for up to an hour[1], with a session lasting one to three hours[2], producing a reduction in the fat thickness in the treated area. Animal and human studies have shown a reduction in fat thickness between 20% and 80% over 3 months following treatment[3]. The device sucks the skin and underlying fat into a cup[4]. More than one treatment can be used, but the results of the second treatment are not as dramatic as the first[5]. CoolSculpting is considered an alternative to liposuction, which is the most common type of plastic surgery.
2 How does CoolSculpting work?
The device removes heat from the skin at a constant rate, rather than chilling to a particular temperature. While the underlying mechanism is unclear[3], the current theory is that chilling fat tissues to just below freezing triggers inflammation of the fat cells (Panniculitis) and then triggers natural cell death in the fat cells (apoptosis). The inflammation starts 3 days after treatment, peaking at 30 days, with some residual inflammation seen after 90 days and the number of fat cells declining over the 90 day period[6].
3 What about frostbite?
A common concern is frostbite, or other damage to the skin. This is not a problem, as you need far colder temperatures to cause that type of damage. CoolSculpting uses temperatures that do not immediately kill off the fat cells, but rather trigger the natural process of cell death(apoptosis). That's why CoolSculpting takes weeks or months for the full effect to be seen.
4 CoolScuplting compared with Cryosurgery
CoolScuplting is quite different to Cryosurgery, which uses cold to kill off tissue, such as tumors. Typically cryosurgery uses far lower temperatures (-20c/-4f to -40c/-40f) and immediately kills off the living cells (necrosis) [7]. Cell damage is caused by temperatures below -10c/14f and CoolSculpting only drops the temperature to around -1c/31f.
5 Side effects of CoolSculpting
There have been no serious side effects reported so far[3]. The skin being treated goes red, with some bruising and numbness. I suspect that the bruising may be because the CoolSculpting device sucks[8][4] the fat against the cooling device. These problems normally resolve within a week. Studies have shown no changes in blood lipid levels or liver function[1]. The numbness is not associated with nerve damage[4].
6 Weight Loss or Spot Reduction?
CoolSculpting reduces the fat thickness in the limited area that is treated rather than producing overall weight loss[3]. CoolSculpting does not seem to be effective in obese people, though it may simply be harder to observe the effects[3]. It's worth noting that CoolSculpting reduces the fat thickness in people who have a stable weight; in other words, you don't need to be on a diet for it to work.
7 How long does it take to work?
The effects of CoolSculpting should start within a few weeks, but the full effect may take 3-4 months[6].
8 DIY CoolSculpting
Having reviewed the evidence for the commercial CoolSculpting, I wondered if it would be possible to replicate the effects by simply applying ice to the skin. The levels of fat on my legs are noticeably lower than other parts of my body, which might be the result of regular icing. There is evidence that applying ice to the skin produces an inflammation response in just a few minutes[1], so this approach seems viable.
8.1 Testing DIY CoolSculpting
So I undertook a simple experiment and applied a bag of ice to the right side of my abdomen for 1-3 hours a day for two weeks. I generally did this in the evenings, applying the ice while watching TV or reading. While the ice is initially uncomfortable and cold, this sensation disappears in a couple of minutes. It also seems that after the first few times the ice is applied, the discomfort is far less.
8.2 Results of DIY CoolSculpting
At the end of the two weeks the fat thickness on the right side was noticeably thinner than the left side. The difference seemed to increase in the week following termination of the icing. At this point I started icing the left side to regain symmetry.
9 References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 CoolSculpting for subcutaneous fat layer red... [Lasers Surg Med. 2009] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20014262
- Jump up ↑ CoolSculpting - Patient FAQs http://www.coolsculpting.com/heres-the-skinny/patient-faq/
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 CoolSculpting for reduction of excess a... [Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20123423
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, Volume 33, Number 4 - SpringerLink http://www.springerlink.com/content/3h17qp3gk314ut17/
- Jump up ↑ Non-invasive CoolSculpting for body contouri... [Lasers Surg Med. 2012] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22334296
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 CoolSculpting for noninvasive fat cell destruc... [Dermatol Surg. 2009] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19614940
- Jump up ↑ All About Cryosurgery http://hassam.hubpages.com/hub/All-About
- Jump up ↑ CoolSculpting http://www.newmanmdplasticsurgery.com/CoolSculpting.html