Difference between revisions of "NSAIDs and Running"
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
User:Fellrnr (User talk:Fellrnr | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DISPLAYTITLE: NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Aspirin) and Acetaminophen/Paracetamol for runners, impairs healing and interferes with hydration}} | {{DISPLAYTITLE: NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Aspirin) and Acetaminophen/Paracetamol for runners, impairs healing and interferes with hydration}} | ||
[[File:Extra Strength Tylenol and Tylenol PM.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Acetaminophen (brand names Tylenol, aspirin-free Anacin, Excedrin, and numerous cold medicines)]] | [[File:Extra Strength Tylenol and Tylenol PM.jpg|right|thumb|200px|Acetaminophen (brand names Tylenol, aspirin-free Anacin, Excedrin, and numerous cold medicines)]] | ||
| − | NSAIDs are generally unhelpful for runners, masking the symptoms while impairing healing, interfering with hydration and can be life threatening. Risks include kidney failure, heart attacks, strokes, intestinal damage, and liver failure. The most common NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) are Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), Naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and Aspirin. They work by inhibiting a particular enzyme ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclooxygenase Cyclooxygenase]) which reduces pain, fever and inflammation. Ibuprofen use is so common among runners that it is sometimes called "Vitamin I"<ref name="VitaminI"/>, with one study finding about 60% of runners using NSAIDs during training<ref name="JoslinLloyd2013"/>. This is unsurprising given the estimates of injury rates in runners varying between 20% and 80%<ref name=" | + | NSAIDs are generally unhelpful for runners, masking the symptoms while impairing healing, interfering with hydration and can be life threatening. Risks include kidney failure, heart attacks, strokes, intestinal damage, and liver failure. The most common NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) are Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), Naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and Aspirin. They work by inhibiting a particular enzyme ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyclooxygenase Cyclooxygenase]) which reduces pain, fever and inflammation. Ibuprofen use is so common among runners that it is sometimes called "Vitamin I"<ref name="VitaminI"/>, with one study finding about 60% of runners using NSAIDs during training<ref name="JoslinLloyd2013"/>. This is unsurprising given the estimates of injury rates in runners varying between 20% and 80%<ref name="vanGent-2007"/>. This article also covers Acetaminophen (also called Paracetamol), though it's not technically an NSAID. |
| − | + | =NSAIDs and Healing= | |
The inflammation response of our bodies is a key part of the healing process. Using NSAIDs to reduce the inflammation has been shown to impair healing in different tissue types: | The inflammation response of our bodies is a key part of the healing process. Using NSAIDs to reduce the inflammation has been shown to impair healing in different tissue types: | ||
* '''Muscles'''<ref name="MuscleTrappe"/>. A 2001 study showed that Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen reduce [[Muscle|muscle]] growth after eccentric exercise. Another study<ref name="muscle"/> on muscle damage and NSAIDs showed impaired recovery in the early stages of healing. There was some increased [[Protein]] synthesis with NSAIDs in latter stages of healing, but the muscles were still weaker 28 days after injury. Other studies<ref name="muscle2"/><ref name="muscle3"/> have shown that four days after injury, NSAIDs resulted in very little muscle regeneration compared with no drugs. | * '''Muscles'''<ref name="MuscleTrappe"/>. A 2001 study showed that Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen reduce [[Muscle|muscle]] growth after eccentric exercise. Another study<ref name="muscle"/> on muscle damage and NSAIDs showed impaired recovery in the early stages of healing. There was some increased [[Protein]] synthesis with NSAIDs in latter stages of healing, but the muscles were still weaker 28 days after injury. Other studies<ref name="muscle2"/><ref name="muscle3"/> have shown that four days after injury, NSAIDs resulted in very little muscle regeneration compared with no drugs. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* '''Cartilage. ''' NSAIDs have been shown<ref name="CartilageRabbit"/> to impair the healing of bone and cartilage in rabbits. | * '''Cartilage. ''' NSAIDs have been shown<ref name="CartilageRabbit"/> to impair the healing of bone and cartilage in rabbits. | ||
* '''Bone fractures.''' Tests on rats shows that a NSAID (Celecoxib) in the early stages of bone healing impaired healing, producing a weaker repair.<ref name="bone"/> A study <ref name="BoneLaurence "/> in 2004 declared " Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs continue to be prescribed as analgesics for patients with healing fractures even though these drugs diminish bone formation, healing, and remodeling". | * '''Bone fractures.''' Tests on rats shows that a NSAID (Celecoxib) in the early stages of bone healing impaired healing, producing a weaker repair.<ref name="bone"/> A study <ref name="BoneLaurence "/> in 2004 declared " Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs continue to be prescribed as analgesics for patients with healing fractures even though these drugs diminish bone formation, healing, and remodeling". | ||
| − | + | ==Counterpoint== | |
While there is extensive experimental evidence for NSAIDs impairing healing, there are also some studies that show no change with NSAID use, and a few that indicated improved healing. For instance, one study<ref name="LigamentImprovement"/> showed that using an NSAID for 6 days after injury resulted in a 42% increased ligament strength at day 14, though there was no change by day 21. Another study<ref name="LigamentUninjuredImprovement"/> showed that an NSAID did not change ligament healing, but did improve the strength of the uninjured ligaments. However, my reading indicates that the preponderance of evidence shows NSAIDs impair healing. | While there is extensive experimental evidence for NSAIDs impairing healing, there are also some studies that show no change with NSAID use, and a few that indicated improved healing. For instance, one study<ref name="LigamentImprovement"/> showed that using an NSAID for 6 days after injury resulted in a 42% increased ligament strength at day 14, though there was no change by day 21. Another study<ref name="LigamentUninjuredImprovement"/> showed that an NSAID did not change ligament healing, but did improve the strength of the uninjured ligaments. However, my reading indicates that the preponderance of evidence shows NSAIDs impair healing. | ||
| − | + | ==Ice, Inflammation and Healing== | |
If NSAIDs are bad for healing, should we treat with ice? So far I have found no definitive studies, but ice has a different mechanism of action from NSAIDs. By cooling the tissues, ice temporarily reduces swelling, thereby flushing the wound. If applied for a longer period of time, ice will produce a periodic increase in blood supply that creates a further flushing effect. I have found that ice can produce dramatic improvements in healing speed. See [[Cryotherapy - Ice for Healing]] for more details. There is no evidence that ice reduces any of the inflammation processes. | If NSAIDs are bad for healing, should we treat with ice? So far I have found no definitive studies, but ice has a different mechanism of action from NSAIDs. By cooling the tissues, ice temporarily reduces swelling, thereby flushing the wound. If applied for a longer period of time, ice will produce a periodic increase in blood supply that creates a further flushing effect. I have found that ice can produce dramatic improvements in healing speed. See [[Cryotherapy - Ice for Healing]] for more details. There is no evidence that ice reduces any of the inflammation processes. | ||
| + | =Turmeric as an NSAID= | ||
| + | Turmeric is an anti-inflammatory<ref name="Sahebkar2014"/><ref name="PanahiSahebkar2012"/> that is often considered an alternative to more common NSAIDs. Turmeric has been medicinally used for 1000s of years<ref name="Benzie-"/> and even in large doses turmeric shows low toxicity<ref name="Hsu-2007"/><ref name="Cheng-2001"/><ref name="Chandran-2012"/><ref name="GanigerMalleshappa2007"/> with only a few studies finding nausea and diarrhea<ref name="Hsu-2007"/> or abdominal pain<ref name="Kuptniratsaikul-2014"/>. Turmeric has poor bioavailability<ref name="Anand-2010"/><ref name="AnandKunnumakkara2007"/>, but versions with improved bioavailability are being developed such as Flexofytol<ref name="AppelboomMaes2014"/> or Meriva<ref name="Drobnic-2014"/>. Like other NSAIDs, Turmeric is an effective pain reliever (analgesic)<ref name="Agarwal-2011"/><ref name="Panahi-2014"/><ref name="Kuptniratsaikul-2009"/><ref name="Zhu-2014"/> and it may be effective in treating [[Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness]]<ref name="Nicol-2015"/><ref name="Drobnic-2014"/><ref name="McFarlinVenable2016"/><ref name="TanabeMaeda2015"/><ref name="Davis-2007"/><ref name="Kawanishi-2013"/>. Studies of Turmeric and turmeric derivatives as treatments for osteoarthritis<ref name="Henrotin-2014"/><ref name="Kuptniratsaikul-2014"/> and rheumatoid arthritis<ref name="Chandran-2012"/> show promising results. Digestive problems, a common side effect of NSAIDs, are believed to be because most NSAIDs inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes<ref name="Bertolini-2002"/>. COX-2 is predominantly responsible for inflammation where COX-1 helps maintain the digestive system<ref name="Hawkey-2001"/>. Selectively inhibiting just COX-2 may have the benefits of NSAIDS without the digestive issues<ref name="FutakiTakahashi1994"/><ref name="Hawkey1999"/><ref name="Hawkey-2001"/>. Studies have found that Turmeric is a COX-2 inhibitor<ref name="Moini Zanjani-2014"/><ref name="Moriyuki-2010"/><ref name="Ireson-2001"/><ref name="Lev-Ari-2006"/><ref name="Plummer-1999"/>, and turmeric preferentially inhibits COX-2 over COX-1<ref name="RamsewakDeWitt2000"/>. Turmeric has ~36% COX-1 inhibition and ~77% COX-2 inhibition, while aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen had 41-52% COX-1 inhibition and ~30-40% COX-2 inhibition<ref name="RamsewakDeWitt2000"/>. Diferuloylmethane (Curcumin) is the main active ingredient in turmeric<ref name="Anand-2010"/><ref name="Henrotin-2010"/>, though it also includes monodemethoxycurcumin (curcumin II) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (curcumin III)<ref name="RamsewakDeWitt2000"/>. Concentrations of Diferuloylmethane typically peak 1-2 hours after consumption and decline within 12 hours<ref name="Cheng-2001"/><ref name="Agarwal-2011"/>. | ||
=NSAIDs and Acute kidney failure= | =NSAIDs and Acute kidney failure= | ||
Kidney failure while running is extremely rare, and seems to require multiple factors to come together. Looking at the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comrades_Marathon Comrades Marathon], a 90 Km/56 Mile ultramarathon in South Africa, there have only been 19 cases of kidney failure between 1969 and 1986, it even though thousands of people participate each year<ref name="rhabdo1"/>. The following are considered factors in acute kidney failure related to running. | Kidney failure while running is extremely rare, and seems to require multiple factors to come together. Looking at the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comrades_Marathon Comrades Marathon], a 90 Km/56 Mile ultramarathon in South Africa, there have only been 19 cases of kidney failure between 1969 and 1986, it even though thousands of people participate each year<ref name="rhabdo1"/>. The following are considered factors in acute kidney failure related to running. | ||
| Line 34: | Line 36: | ||
* The most common NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen (Paracetamol), and Aspirin) are unlikely to help with DOMS. | * The most common NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen (Paracetamol), and Aspirin) are unlikely to help with DOMS. | ||
* There is some evidence that Naproxen may be more effective than the common NSAIDs. There is not enough evidence to reach a conclusion on Diclofenac, Codeine, Rofecoxib, Ketoprofen, or Bromelain. | * There is some evidence that Naproxen may be more effective than the common NSAIDs. There is not enough evidence to reach a conclusion on Diclofenac, Codeine, Rofecoxib, Ketoprofen, or Bromelain. | ||
| + | * There is also some evidence that Turmeric may help with DOMS. | ||
* If an NSAID is taken for DOMS, it should probably be taken immediately after the damaging exercise rather than waiting until the soreness develops. | * If an NSAID is taken for DOMS, it should probably be taken immediately after the damaging exercise rather than waiting until the soreness develops. | ||
| − | * It seems likely that taking an NSAID for DOMS will reduce the muscular growth that would normally occur as part of the recovery. | + | * It seems likely that taking an NSAID for DOMS will reduce the muscular growth that would normally occur as part of the recovery. In one study, rabbits treated with flurbiprofen after DOMS inducing exercise regained more strength after 3-7 days, but between days 7 and 28 days the treated rabbits became weaker while the controls became stronger<ref name="Mishra-1995"/>. This is only one study, and on animals, but it is rather troubling as none of the human studies look at the results over this time period. |
| − | |||
==A Summary of the Research on NSAIDs and DOMS== | ==A Summary of the Research on NSAIDs and DOMS== | ||
The table below summarizes the research I located on the effect of NSAIDs on DOMS in humans. I've only considered the primary DOMS markers of soreness (pain) and weakness, rather than including things like blood enzymes. For each NSAID I've shown how many studies show an improvement and how many studies show no effect. | The table below summarizes the research I located on the effect of NSAIDs on DOMS in humans. I've only considered the primary DOMS markers of soreness (pain) and weakness, rather than including things like blood enzymes. For each NSAID I've shown how many studies show an improvement and how many studies show no effect. | ||
| Line 88: | Line 90: | ||
| 1xNo Effect<ref name="Stone-2002"/> | | 1xNo Effect<ref name="Stone-2002"/> | ||
| | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Turmeric | ||
| + | | 2xImproved<ref name="Nicol-2015"/><ref name="Drobnic-2014"/> | ||
| + | 2xNo Effect<ref name="McFarlinVenable2016"/><ref name="TanabeMaeda2015"/> | ||
| + | | 2xImproved<ref name="TanabeMaeda2015"/><ref name="Davis-2007"/> | ||
|} | |} | ||
=NSAIDs and Intestinal Damage= | =NSAIDs and Intestinal Damage= | ||
| Line 113: | Line 120: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
<references> | <references> | ||
| + | <ref name="Hawkey1999">CJ Hawkey, COX-2 inhibitors, The Lancet, volume 353, issue 9149, 1999, pages 307–314, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/01406736 01406736], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(98)12154-2 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)12154-2]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="FutakiTakahashi1994">N. Futaki, S. Takahashi, M. Yokoyama, I. Arai, S. Higuchi, S. Otomo, NS-398, a new anti-inflammatory agent, selectively inhibits prostaglandin G/H synthase/cyclooxygenase (COX-2) activity in vitro, Prostaglandins, volume 47, issue 1, 1994, pages 55–59, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/00906980 00906980], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0090-6980(94)90074-4 10.1016/0090-6980(94)90074-4]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Bertolini-2002">A. Bertolini, A. Ottani, M. Sandrini, Selective COX-2 inhibitors and dual acting anti-inflammatory drugs: critical remarks., Curr Med Chem, volume 9, issue 10, pages 1033-43, May 2002, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12733982 12733982]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Zhu-2014">X. Zhu, Q. Li, R. Chang, D. Yang, Z. Song, Q. Guo, C. Huang, Curcumin alleviates neuropathic pain by inhibiting p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase activity-regulated expression of BDNF and cox-2 in a rat model., PLoS One, volume 9, issue 3, pages e91303, 2014, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091303 10.1371/journal.pone.0091303], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24603592 24603592]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Plummer-1999">SM. Plummer, KA. Holloway, MM. Manson, RJ. Munks, A. Kaptein, S. Farrow, L. Howells, Inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the NIK/IKK signalling complex., Oncogene, volume 18, issue 44, pages 6013-20, Oct 1999, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202980 10.1038/sj.onc.1202980], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10557090 10557090]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Lev-Ari-2006">S. Lev-Ari, A. Starr, A. Vexler, V. Karaush, V. Loew, J. Greif, E. Fenig, D. Aderka, R. Ben-Yosef, Inhibition of pancreatic and lung adenocarcinoma cell survival by curcumin is associated with increased apoptosis, down-regulation of COX-2 and EGFR and inhibition of Erk1/2 activity., Anticancer Res, volume 26, issue 6B, pages 4423-30, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17201164 17201164]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="RamsewakDeWitt2000">R.S. Ramsewak, D.L. DeWitt, M.G. Nair, Cytotoxicity, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Curcumins I–III from Curcuma longa, Phytomedicine, volume 7, issue 4, 2000, pages 303–308, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/09447113 09447113], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0944-7113(00)80048-3 10.1016/S0944-7113(00)80048-3]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Ireson-2001">C. Ireson, S. Orr, DJ. Jones, R. Verschoyle, CK. Lim, JL. Luo, L. Howells, S. Plummer, R. Jukes, Characterization of metabolites of the chemopreventive agent curcumin in human and rat hepatocytes and in the rat in vivo, and evaluation of their ability to inhibit phorbol ester-induced prostaglandin E2 production., Cancer Res, volume 61, issue 3, pages 1058-64, Feb 2001, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11221833 11221833]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Moriyuki-2010">K. Moriyuki, F. Sekiguchi, K. Matsubara, H. Nishikawa, A. Kawabata, Curcumin Inhibits the proteinase-activated receptor-2-triggered prostaglandin E2 production by suppressing cyclooxygenase-2 upregulation and Akt-dependent activation of nuclear factor-κB in human lung epithelial cells., J Pharmacol Sci, volume 114, issue 2, pages 225-9, 2010, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20838026 20838026]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Kawanishi-2013">N. Kawanishi, K. Kato, M. Takahashi, T. Mizokami, Y. Otsuka, A. Imaizumi, D. Shiva, H. Yano, K. Suzuki, Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress following downhill running-induced muscle damage., Biochem Biophys Res Commun, volume 441, issue 3, pages 573-8, Nov 2013, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.119 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.119], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24184481 24184481]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Davis-2007">JM. Davis, EA. Murphy, MD. Carmichael, MR. Zielinski, CM. Groschwitz, AS. Brown, JD. Gangemi, A. Ghaffar, EP. Mayer, Curcumin effects on inflammation and performance recovery following eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage., Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, volume 292, issue 6, pages R2168-73, Jun 2007, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00858.2006 10.1152/ajpregu.00858.2006], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17332159 17332159]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="TanabeMaeda2015">Yoko Tanabe, Seiji Maeda, Nobuhiko Akazawa, Asako Zempo-Miyaki, Youngju Choi, Song-Gyu Ra, Atsushi Imaizumi, Yoshihiko Otsuka, Kazunori Nosaka, Attenuation of indirect markers of eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage by curcumin, European Journal of Applied Physiology, volume 115, issue 9, 2015, pages 1949–1957, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/1439-6319 1439-6319], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3170-4 10.1007/s00421-015-3170-4]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="McFarlinVenable2016">Brian K. McFarlin, Adam S. Venable, Andrea L. Henning, Jill N. Best Sampson, Kathryn Pennel, Jakob L. Vingren, David W. Hill, Reduced Inflammatory and Muscle Damage Biomarkers following Oral Supplementation with Bioavailable Curcumin, BBA Clinical, 2016, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/22146474 22146474], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.02.003 10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.02.003]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Kuptniratsaikul-2014">V. Kuptniratsaikul, P. Dajpratham, W. Taechaarpornkul, M. Buntragulpoontawee, P. Lukkanapichonchut, C. Chootip, J. Saengsuwan, K. Tantayakom, S. Laongpech, Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts compared with ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter study., Clin Interv Aging, volume 9, pages 451-8, 2014, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S58535 10.2147/CIA.S58535], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24672232 24672232]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Drobnic-2014">F. Drobnic, J. Riera, G. Appendino, S. Togni, F. Franceschi, X. Valle, A. Pons, J. Tur, Reduction of delayed onset muscle soreness by a novel curcumin delivery system (Meriva): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial., J Int Soc Sports Nutr, volume 11, pages 31, 2014, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-11-31 10.1186/1550-2783-11-31], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24982601 24982601]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Nicol-2015">LM. Nicol, DS. Rowlands, R. Fazakerly, J. Kellett, Curcumin supplementation likely attenuates delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS)., Eur J Appl Physiol, volume 115, issue 8, pages 1769-77, Aug 2015, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3152-6 10.1007/s00421-015-3152-6], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25795285 25795285]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Henrotin-2014">Y. Henrotin, M. Gharbi, Y. Dierckxsens, F. Priem, M. Marty, L. Seidel, A. Albert, E. Heuse, V. Bonnet, Decrease of a specific biomarker of collagen degradation in osteoarthritis, Coll2-1, by treatment with highly bioavailable curcumin during an exploratory clinical trial., BMC Complement Altern Med, volume 14, pages 159, 2014, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-159 10.1186/1472-6882-14-159], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24886572 24886572]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Chandran-2012">B. Chandran, A. Goel, A randomized, pilot study to assess the efficacy and safety of curcumin in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis., Phytother Res, volume 26, issue 11, pages 1719-25, Nov 2012, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ptr.4639 10.1002/ptr.4639], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22407780 22407780]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Moini Zanjani-2014">T. Moini Zanjani, H. Ameli, F. Labibi, K. Sedaghat, M. Sabetkasaei, The Attenuation of Pain Behavior and Serum COX-2 Concentration by Curcumin in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain., Korean J Pain, volume 27, issue 3, pages 246-52, Jul 2014, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.3.246 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.3.246], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25031810 25031810]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="AppelboomMaes2014">Thierry Appelboom, Nathalie Maes, Adelin Albert, A New Curcuma Extract (Flexofytol®) in Osteoarthritis: Results from a Belgian Real-Life Experience, The Open Rheumatology Journal, volume 8, issue 1, 2014, pages 77–81, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/18743129 18743129], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/1874312901408010077 10.2174/1874312901408010077]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Kuptniratsaikul-2009">V. Kuptniratsaikul, S. Thanakhumtorn, P. Chinswangwatanakul, L. Wattanamongkonsil, V. Thamlikitkul, Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts in patients with knee osteoarthritis., J Altern Complement Med, volume 15, issue 8, pages 891-7, Aug 2009, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/acm.2008.0186 10.1089/acm.2008.0186], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19678780 19678780]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Panahi-2014">Y. Panahi, AR. Rahimnia, M. Sharafi, G. Alishiri, A. Saburi, A. Sahebkar, Curcuminoid treatment for knee osteoarthritis: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial., Phytother Res, volume 28, issue 11, pages 1625-31, Nov 2014, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5174 10.1002/ptr.5174], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24853120 24853120]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Agarwal-2011">KA. Agarwal, CD. Tripathi, BB. Agarwal, S. Saluja, Efficacy of turmeric (curcumin) in pain and postoperative fatigue after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled study., Surg Endosc, volume 25, issue 12, pages 3805-10, Dec 2011, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00464-011-1793-z 10.1007/s00464-011-1793-z], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21671126 21671126]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="AnandKunnumakkara2007">Preetha Anand, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara, Robert A. Newman, Bharat B. Aggarwal, Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Promises, Molecular Pharmaceutics, volume 4, issue 6, 2007, pages 807–818, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/1543-8384 1543-8384], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/mp700113r 10.1021/mp700113r]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Cheng-2001">AL. Cheng, CH. Hsu, JK. Lin, MM. Hsu, YF. Ho, TS. Shen, JY. Ko, JT. Lin, BR. Lin, Phase I clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions., Anticancer Res, volume 21, issue 4B, pages 2895-900, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11712783 11712783]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Hsu-2007">CH. Hsu, AL. Cheng, Clinical studies with curcumin., Adv Exp Med Biol, volume 595, pages 471-80, 2007, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5_21 10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5_21], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17569225 17569225]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Henrotin-2010">Y. Henrotin, AL. Clutterbuck, D. Allaway, EM. Lodwig, P. Harris, M. Mathy-Hartert, M. Shakibaei, A. Mobasheri, Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes., Osteoarthritis Cartilage, volume 18, issue 2, pages 141-9, Feb 2010, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2009.10.002 10.1016/j.joca.2009.10.002], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19836480 19836480]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Anand-2010">P. Anand, HB. Nair, B. Sung, AB. Kunnumakkara, VR. Yadav, RR. Tekmal, BB. Aggarwal, Design of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles formulation with enhanced cellular uptake, and increased bioactivity in vitro and superior bioavailability in vivo., Biochem Pharmacol, volume 79, issue 3, pages 330-8, Feb 2010, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009.09.003 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.09.003], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19735646 19735646]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="PanahiSahebkar2012">Y. Panahi, A. Sahebkar, S. Parvin, A. Saadat, A randomized controlled trial on the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in patients with chronic sulphur mustard-induced cutaneous complications, Annals of Clinical Biochemistry, volume 49, issue 6, 2012, pages 580–588, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/0004-5632 0004-5632], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1258/acb.2012.012040 10.1258/acb.2012.012040]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Sahebkar2014">Amirhossein Sahebkar, Are Curcuminoids Effective C-Reactive Protein-Lowering Agents in Clinical Practice? Evidence from a Meta-Analysis, Phytotherapy Research, volume 28, issue 5, 2014, pages 633–642, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/0951418X 0951418X], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5045 10.1002/ptr.5045]</ref> | ||
<ref name="bone">JBJS | Dose and Time-Dependent Effects of Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition on Fracture-Healing http://www.jbjs.org/article.aspx?Volume=89&page=500</ref> | <ref name="bone">JBJS | Dose and Time-Dependent Effects of Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition on Fracture-Healing http://www.jbjs.org/article.aspx?Volume=89&page=500</ref> | ||
<ref name="tendon">NSAIDs Inhibit Tendon-to-Bone Healing in Rotator Cuff Repair http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?article=295</ref> | <ref name="tendon">NSAIDs Inhibit Tendon-to-Bone Healing in Rotator Cuff Repair http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?article=295</ref> | ||
| Line 180: | Line 217: | ||
<ref name="ToussaintYang2010">K. Toussaint, X. C. Yang, M. A. Zielinski, K. L. Reigle, S. D. Sacavage, S. Nagar, R. B. Raffa, What do we (not) know about how paracetamol (acetaminophen) works?, Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, volume 35, issue 6, 2010, pages 617–638, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/02694727 02694727], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01143.x 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01143.x]</ref> | <ref name="ToussaintYang2010">K. Toussaint, X. C. Yang, M. A. Zielinski, K. L. Reigle, S. D. Sacavage, S. Nagar, R. B. Raffa, What do we (not) know about how paracetamol (acetaminophen) works?, Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, volume 35, issue 6, 2010, pages 617–638, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/02694727 02694727], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01143.x 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01143.x]</ref> | ||
<ref name="www.fda.gov">FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA strengthens warning that non-aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can cause heart attacks or strokes, http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm451800.htm, Accessed on 25 January 2016</ref> | <ref name="www.fda.gov">FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA strengthens warning that non-aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can cause heart attacks or strokes, http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm451800.htm, Accessed on 25 January 2016</ref> | ||
| − | <ref name="JoslinLloyd2013">Jeremy D Joslin, Jarem B Lloyd, Timur Kotlyar, Susan M Wojcik, NSAID and other analgesic use by endurance runners during training, competition and recovery, South African Journal of Sports Medicine, volume 25, issue 4, 2013, pages 101, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/2078-516X 2078-516X], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.7196/sajsm.495 10.7196/sajsm.495]</ref | + | <ref name="JoslinLloyd2013">Jeremy D Joslin, Jarem B Lloyd, Timur Kotlyar, Susan M Wojcik, NSAID and other analgesic use by endurance runners during training, competition and recovery, South African Journal of Sports Medicine, volume 25, issue 4, 2013, pages 101, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/2078-516X 2078-516X], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.7196/sajsm.495 10.7196/sajsm.495]</ref> |
| − | <ref name=" | + | <ref name="vanGent-2007">RN. van Gent, D. Siem, M. van Middelkoop, AG. van Os, SM. Bierma-Zeinstra, BW. Koes, Incidence and determinants of lower extremity running injuries in long distance runners: a systematic review., Br J Sports Med, volume 41, issue 8, pages 469-80; discussion 480, Aug 2007, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.2006.033548 10.1136/bjsm.2006.033548], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17473005 17473005]</ref> |
| + | <ref name="Benzie-">IFF. Benzie, S. Wachtel-Galor, S. Prasad, BB. Aggarwal, Turmeric, the Golden Spice: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Medicine, PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22593922 22593922]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="GanigerMalleshappa2007">S. Ganiger, H.N. Malleshappa, H. Krishnappa, Geetha Rajashekhar, V. Ramakrishna Rao, Frank Sullivan, A two generation reproductive toxicity study with curcumin, turmeric yellow, in Wistar rats, Food and Chemical Toxicology, volume 45, issue 1, 2007, pages 64–69, ISSN [http://www.worldcat.org/issn/02786915 02786915], doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2006.07.016 10.1016/j.fct.2006.07.016]</ref> | ||
| + | <ref name="Hawkey-2001">CJ. Hawkey, COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors., Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, volume 15, issue 5, pages 801-20, Oct 2001, doi [http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/bega.2001.0236 10.1053/bega.2001.0236], PMID [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11566042 11566042]</ref> | ||
| + | </references> | ||
[[Category:Training]] | [[Category:Training]] | ||
[[Category:Injury]] | [[Category:Injury]] | ||
[[Category:Science]] | [[Category:Science]] | ||
Revision as of 16:59, 24 February 2016
NSAIDs are generally unhelpful for runners, masking the symptoms while impairing healing, interfering with hydration and can be life threatening. Risks include kidney failure, heart attacks, strokes, intestinal damage, and liver failure. The most common NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) are Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), Naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), and Aspirin. They work by inhibiting a particular enzyme (Cyclooxygenase) which reduces pain, fever and inflammation. Ibuprofen use is so common among runners that it is sometimes called "Vitamin I"[1], with one study finding about 60% of runners using NSAIDs during training[2]. This is unsurprising given the estimates of injury rates in runners varying between 20% and 80%[3]. This article also covers Acetaminophen (also called Paracetamol), though it's not technically an NSAID.
Contents
- 1 NSAIDs and Healing
- 2 Turmeric as an NSAID
- 3 NSAIDs and Acute kidney failure
- 4 NSAIDs and Hyponatremia
- 5 NSAIDs causing Heart Attacks or Strokes
- 6 NSAIDs and Infection
- 7 NSAIDs for Pain Reduction
- 8 NSAIDs and DOMS
- 9 NSAIDs and Intestinal Damage
- 10 NSAIDs and Wound Healing
- 11 NSAIDs and Racing
- 12 Longer Term NSAID usage
- 13 Acetaminophen Overdose Danger (AKA Paracetamol, Tylenol)
- 14 Is Acetaminophen an NSAID?
- 15 References
1 NSAIDs and Healing
The inflammation response of our bodies is a key part of the healing process. Using NSAIDs to reduce the inflammation has been shown to impair healing in different tissue types:
- Muscles[4]. A 2001 study showed that Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen reduce muscle growth after eccentric exercise. Another study[5] on muscle damage and NSAIDs showed impaired recovery in the early stages of healing. There was some increased Protein synthesis with NSAIDs in latter stages of healing, but the muscles were still weaker 28 days after injury. Other studies[6][7] have shown that four days after injury, NSAIDs resulted in very little muscle regeneration compared with no drugs.
- Tendons. A primate study[8] showed "a marked decrease in the breaking strength of tendons at four and six weeks in the ibuprofen-treated animals". Another animal study[9] showed treated tendons were 32% weaker than their untested counterparts.
- Bone-Tendon Junctions. An animal study[10] of rotator cuff injuries shows that NSAID usage resulted in injuries that did not heal, and those that did heal were weaker than those without NSAID. To quote from the study "Given that NSAID administration was discontinued after 14 days yet affected load-to-failure eight weeks following repair, it appears that inhibition of the early events in the inflammatory cascade has a lasting negative effect on tendon-to-bone healing," Dr. Rodeo said.
- Cartilage. NSAIDs have been shown[11] to impair the healing of bone and cartilage in rabbits.
- Bone fractures. Tests on rats shows that a NSAID (Celecoxib) in the early stages of bone healing impaired healing, producing a weaker repair.[12] A study [13] in 2004 declared " Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs continue to be prescribed as analgesics for patients with healing fractures even though these drugs diminish bone formation, healing, and remodeling".
1.1 Counterpoint
While there is extensive experimental evidence for NSAIDs impairing healing, there are also some studies that show no change with NSAID use, and a few that indicated improved healing. For instance, one study[14] showed that using an NSAID for 6 days after injury resulted in a 42% increased ligament strength at day 14, though there was no change by day 21. Another study[15] showed that an NSAID did not change ligament healing, but did improve the strength of the uninjured ligaments. However, my reading indicates that the preponderance of evidence shows NSAIDs impair healing.
1.2 Ice, Inflammation and Healing
If NSAIDs are bad for healing, should we treat with ice? So far I have found no definitive studies, but ice has a different mechanism of action from NSAIDs. By cooling the tissues, ice temporarily reduces swelling, thereby flushing the wound. If applied for a longer period of time, ice will produce a periodic increase in blood supply that creates a further flushing effect. I have found that ice can produce dramatic improvements in healing speed. See Cryotherapy - Ice for Healing for more details. There is no evidence that ice reduces any of the inflammation processes.
2 Turmeric as an NSAID
Turmeric is an anti-inflammatory[16][17] that is often considered an alternative to more common NSAIDs. Turmeric has been medicinally used for 1000s of years[18] and even in large doses turmeric shows low toxicity[19][20][21][22] with only a few studies finding nausea and diarrhea[19] or abdominal pain[23]. Turmeric has poor bioavailability[24][25], but versions with improved bioavailability are being developed such as Flexofytol[26] or Meriva[27]. Like other NSAIDs, Turmeric is an effective pain reliever (analgesic)[28][29][30][31] and it may be effective in treating Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness[32][27][33][34][35][36]. Studies of Turmeric and turmeric derivatives as treatments for osteoarthritis[37][23] and rheumatoid arthritis[21] show promising results. Digestive problems, a common side effect of NSAIDs, are believed to be because most NSAIDs inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes[38]. COX-2 is predominantly responsible for inflammation where COX-1 helps maintain the digestive system[39]. Selectively inhibiting just COX-2 may have the benefits of NSAIDS without the digestive issues[40][41][39]. Studies have found that Turmeric is a COX-2 inhibitor[42][43][44][45][46], and turmeric preferentially inhibits COX-2 over COX-1[47]. Turmeric has ~36% COX-1 inhibition and ~77% COX-2 inhibition, while aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen had 41-52% COX-1 inhibition and ~30-40% COX-2 inhibition[47]. Diferuloylmethane (Curcumin) is the main active ingredient in turmeric[24][48], though it also includes monodemethoxycurcumin (curcumin II) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (curcumin III)[47]. Concentrations of Diferuloylmethane typically peak 1-2 hours after consumption and decline within 12 hours[20][28].
3 NSAIDs and Acute kidney failure
Kidney failure while running is extremely rare, and seems to require multiple factors to come together. Looking at the Comrades Marathon, a 90 Km/56 Mile ultramarathon in South Africa, there have only been 19 cases of kidney failure between 1969 and 1986, it even though thousands of people participate each year[49]. The following are considered factors in acute kidney failure related to running.
- Dehydration. Exercise reduces blood flow to the kidneys and dehydration makes this worse.
- NSAIDs. NSAIDs also reduce blood flow to the kidneys[50]. NSAIDs reduce prostaglandin production, and prostaglandins are vital to maintaining blood flow to the kidneys. While NSAIDs are considered safe drugs, NSAIDs are associated with a relatively high incidence of adverse drug reactions involving the kidneys. Generally, NSAID side effects are restricted to individuals with predisposition to kidney problems, so extra care should be taken if you have a history of kidney problems. However, athletes push their bodies to extremes, so what applies to the general population may not be valid for runners. One runner was told[51] by doctors that 2400mg Ibuprofen in an ultramarathon was a contributing factor to his kidney failure.
- Rhabdomyolysis. All strenuous exercise causes some muscle damage, but this is generally resolved without a problem. However large amounts of a Protein called myoglobin from damaged muscle can cause a condition called rhabdomyolysis (AKA 'rhabdo'). While serious rhabdomyolysis is rare, it is worth understanding one key symptom, which is low volume, dark urine, often likened to 'coca-cola'. The other symptoms include severe, incapacitating muscle pain and elevated levels of creatine kinase (CK) in the blood (which requires a specialist test). Some individuals[52] have a genetic condition that makes rhabdomyolysis possible after relatively moderate exercise. Rhabdomyolysis is also more likely after eccentric exercise, such as Downhill Running.
- Sickness. A viral or bacterial infection is often a factor in exercise related kidney failure.
Looking at the analysis[50] of nine cases of continued kidney failure in Comrades Marathon, seven had taken NSAIDs, four may have had a viral or bacterial infection. The combination of dehydration, rhabdomyolysis, infection and NSAIDs are a perfect storm for the kidneys.
4 NSAIDs and Hyponatremia
The kidneys are responsible for removing excess fluid from the blood as well as excreting or withholding sodium. If kidney function is compromised, then this can result in Hyponatremia, which can be fatal. Some studies[53][54][55] have shown a correlation between NSAID use in races and Hyponatremia, but others[56][57] have not. Using NSAIDs when hydration is a concern increases the risk of problems occuring.
5 NSAIDs causing Heart Attacks or Strokes
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warnings that non-aspirin NSAIDs increase the risk of a heart attack or stroke[58]. The risk appears to be related to ongoing usage rather than single doses, with the risk increasing in the first weeks of usage and the risk may increase with prolonged usage. The increased risk is dose dependent (taking more has a greater risk), and the includes those without heart disease or risk factors for heart disease. Not surprisingly, those already with a higher risk of heart disease or stroke have a proportionately higher risk with NSAID usage.
6 NSAIDs and Infection
Because a bacterial or viral infection puts more stress on the body, including the kidneys, taking NSAIDs and continuing to run increases your risk of complications. If the sickness is too bad to run without NSAIDs, you probably shouldn't run.
7 NSAIDs for Pain Reduction
The primary purpose of NSAIDs is generally for reducing pain, and they are remarkably effective at achieving this. If you need a painkiller, acetaminophen is probably a better choice than ibuprofen, though be careful as it's easy to overdose on Acetaminophen (see below). Acetaminophen has limited anti-inflammatory properties, so it shouldn't impair healing as much as ibuprofen, but it is still good as a painkiller. Combining acetaminophen or other NSAIDs with Caffeine further improves their painkilling effectiveness. After a major race I can sometimes have so much leg pain that I can't sleep and a little acetaminophen can make all the difference. While the acetaminophen may impair healing somewhat I believe the trade-off in improved sleep is worthwhile. After all, the lack of sleep itself will impair healing, so it's a reasonable compromise.
8 NSAIDs and DOMS
Main article: Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness
Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness (DOMS) generally occurs between 24 and 72 hours after unusual or severe exercise, such as racing a marathon or Downhill Running. The use of NSAIDs to prevent or treat DOMS has been widely researched, with somewhat mixed results. Even scholarly reviews of the research have differing conclusions[59] [60] [61][62]. My conclusions based on the available research are:
- The most common NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen (Paracetamol), and Aspirin) are unlikely to help with DOMS.
- There is some evidence that Naproxen may be more effective than the common NSAIDs. There is not enough evidence to reach a conclusion on Diclofenac, Codeine, Rofecoxib, Ketoprofen, or Bromelain.
- There is also some evidence that Turmeric may help with DOMS.
- If an NSAID is taken for DOMS, it should probably be taken immediately after the damaging exercise rather than waiting until the soreness develops.
- It seems likely that taking an NSAID for DOMS will reduce the muscular growth that would normally occur as part of the recovery. In one study, rabbits treated with flurbiprofen after DOMS inducing exercise regained more strength after 3-7 days, but between days 7 and 28 days the treated rabbits became weaker while the controls became stronger[63]. This is only one study, and on animals, but it is rather troubling as none of the human studies look at the results over this time period.
8.1 A Summary of the Research on NSAIDs and DOMS
The table below summarizes the research I located on the effect of NSAIDs on DOMS in humans. I've only considered the primary DOMS markers of soreness (pain) and weakness, rather than including things like blood enzymes. For each NSAID I've shown how many studies show an improvement and how many studies show no effect.
| NSAID | Soreness | Weakness |
|---|---|---|
| Ibuprofen | 2xImproved[64][65] | 1xMaybe[64] |
| Ibuprofen Gel | 1xNo Effect[73] | |
| Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) | 2xNo Effect[74][75] | |
| Aspirin | 2xImproved[76][77] | 2xNo Effect[76][77] |
| Naproxen | 4xImproved[78][79][80][81]
1xNo Effect[82] |
3xImproved[78][79][80]
1xNo Effect[82] |
| Diclofenac | Possible slight reduction[83] | |
| Codeine | 1xNo Effect[74] | |
| Rofecoxib | 1xNo Effect[84] | |
| Ketoprofen | 1xImproved[85] | 1xImproved[85] |
| Bromelain | 1xNo Effect[72] | |
| Turmeric | 2xImproved[32][27] | 2xImproved[34][35] |
9 NSAIDs and Intestinal Damage
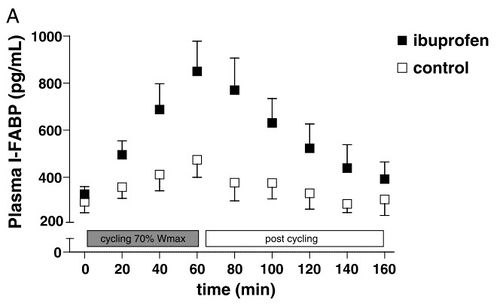
As little as one hour of intense cycling can result in indications of small intestinal damage[86]. This is believed to be due to the redirection of blood away from the digestive system and towards the active muscles. These markers are significantly higher if 400mg ibuprofen (the standard single adult dose) is taken before the exercise[87]. The marker used is Plasma Intestinal Fatty Acid Binding Protein which is an early marker of intestinal necrosis[88].
10 NSAIDs and Wound Healing
Main article: Popping Blisters
Ibuprofen, and possibly other NSAIDs, impair wound healing and should be avoided[89][90].
11 NSAIDs and Racing
Taking NSAIDs in ultramarathon events can improve performance by reducing pain and acute inflammation, but doing so represents a significant risk. There is some evidence[91] [92] that many runners taking NSAIDs have the same level of pain and greater damage markers compared with non-users. This may be because the runners push themselves to a similar level of pain, with the NSAIDs allowing them to do more damage.
- It seems likely that NSAIDs will increase the risk of injury rather than reducing it, as the symptoms of damage will be masked.
- The most common NSAID for racing seems to be ibuprofen. I've not seen any evidence of the relative effectiveness of different NSAIDs on performance.
- It is better to take liquid ibuprofen than tablets or capsules. The tablets and capsules take longer to dissolve and if you have a digestive problem they may not be fully absorbed. You can chew the tablets, but this is unpleasant and ibuprofen can irritate your mouth and throat slightly, so the liquid form is best. It's obviously harder to transport, but you can fill an old film canister with a dose.
- Before an ultramarathon race, you should think through under what circumstances you will consider using NSAIDs and what dosage. Make sure your crew knows that you're taking NSAIDs in case anything happens.
- Extra care should be taken when NSAIDs are used in combination with dehydration, sickness or running the causes serious muscle damage.
- Taking NSAIDs in marathon or shorter races is probably ineffective as the level of damage seen is not as great as in ultramarathon events.
- If you need NSAIDs to start a race, you probably should not compete.
12 Longer Term NSAID usage
Using NSAIDs for longer periods of time can lead to serious health problems and can be fatal. I have a running friend who had a bleeding ulcer from using Ibuprofen, which is a known[93] side effect. The likelihood of a bleeding or perforated ulcer goes up with time, from 1% after 3-6 months, to 2-4% after 12 months. 35% of long term Ibuprofen users get an ulcer[94], which are grim odds.
13 Acetaminophen Overdose Danger (AKA Paracetamol, Tylenol)
Acetaminophen does not have the same risk of ulcers, but it is linked to liver damage, especially in those who drink alcohol. Acetaminophen is the leading cause of acute liver failure[95][96]. There are concerns[97] that even the standard dose can cause changes in liver function. Acetaminophen can cause delayed symptoms[96], with people seeking medical help up to 5 days after the overdose (20% < 12 hours, 35% 12-24 hours, 45% 24 hours+). Overdoses of Acetaminophen can be caused by taking slightly too much over several days, with the toxicity building up[96]. This problem is again exacerbated by those taking alcohol with Acetaminophen[96]. (One factor that increases the risk is that some common medications, such as cold remedies, include Acetaminophen. If people do not add in the dose of Acetaminophen from these other sources, it is easy to unwittingly exceed the safe dosage.)
14 Is Acetaminophen an NSAID?
Acetaminophen (also called paracetamol) is generally not classified as an NSAID[98]. While Acetaminophen has limited anti-inflammatory properties, it shares the same mechanism of action with most NSAIDs of inhibiting the COX enzyme and the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis[99][100][101][102]. Therefore, this article includes Acetaminophen in with NSAIDs.
15 References
- ↑ Urban Dictionary: Vitamin I http://www.urbandictionary.com/define.php?term=Vitamin%20I
- ↑ Jeremy D Joslin, Jarem B Lloyd, Timur Kotlyar, Susan M Wojcik, NSAID and other analgesic use by endurance runners during training, competition and recovery, South African Journal of Sports Medicine, volume 25, issue 4, 2013, pages 101, ISSN 2078-516X, doi 10.7196/sajsm.495
- ↑ RN. van Gent, D. Siem, M. van Middelkoop, AG. van Os, SM. Bierma-Zeinstra, BW. Koes, Incidence and determinants of lower extremity running injuries in long distance runners: a systematic review., Br J Sports Med, volume 41, issue 8, pages 469-80; discussion 480, Aug 2007, doi 10.1136/bjsm.2006.033548, PMID 17473005
- ↑ Skeletal Muscle PGF2αand PGE2 in Response to Eccentric Resistance Exercise: Influence of Ibuprofen and Acetaminophen http://jcem.endojournals.org/content/86/10/5067.long
- ↑ An In Vitro Investigation Into the Effects of Repetitive Motion and Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Medication on Human Tendon Fibroblasts http://ajs.sagepub.com/content/23/1/119
- ↑ Cost-conscious prescribing of nonsteroidal anti-in... [Arch Intern Med. 1992] - PubMed result http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1417372
- ↑ Sports Injuries - NSAIDs: Why We Do Not Recommend Them http://www.caringmedical.com/sports_injury/nsaids.asp
- ↑ Oral ibuprofen: evaluation of its effect on peritendinous adhesions and the breaking strength of a tenorrhaphy. [J Hand Surg Am. 1986] - PubMed result http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3511134#
- ↑ A cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor impairs ligament heal... [Am J Sports Med. 2001 Nov-Dec] - PubMed result http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11734496?dopt=Abstract&holding=npg
- ↑ NSAIDs Inhibit Tendon-to-Bone Healing in Rotator Cuff Repair http://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article.asp?article=295
- ↑ Effect of ibuprofen on the healing and remodeling of bone and articular cartilage in the rabbit temporomandibular joint http://www.joms.org/article/0278-2391%2892%2990276-6/abstract
- ↑ JBJS | Dose and Time-Dependent Effects of Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition on Fracture-Healing http://www.jbjs.org/article.aspx?Volume=89&page=500
- ↑ Effects of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Bone Formation and Soft-Tissue Healing -- Dahners and Mullis 12 (3): 139 -- Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://www.jaaos.org/cgi/content/abstract/12/3/139
- ↑ The effect of a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug... [Am J Sports Med. 1988 Nov-Dec] - PubMed result http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3239621?dopt=Abstract&holding=npg
- ↑ The influence of a cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitor on i... [Am J Sports Med. 2003 Jul-Aug] - PubMed result http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12860547
- ↑ Amirhossein Sahebkar, Are Curcuminoids Effective C-Reactive Protein-Lowering Agents in Clinical Practice? Evidence from a Meta-Analysis, Phytotherapy Research, volume 28, issue 5, 2014, pages 633–642, ISSN 0951418X, doi 10.1002/ptr.5045
- ↑ Y. Panahi, A. Sahebkar, S. Parvin, A. Saadat, A randomized controlled trial on the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in patients with chronic sulphur mustard-induced cutaneous complications, Annals of Clinical Biochemistry, volume 49, issue 6, 2012, pages 580–588, ISSN 0004-5632, doi 10.1258/acb.2012.012040
- ↑ IFF. Benzie, S. Wachtel-Galor, S. Prasad, BB. Aggarwal, Turmeric, the Golden Spice: From Traditional Medicine to Modern Medicine, PMID 22593922
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 CH. Hsu, AL. Cheng, Clinical studies with curcumin., Adv Exp Med Biol, volume 595, pages 471-80, 2007, doi 10.1007/978-0-387-46401-5_21, PMID 17569225
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 AL. Cheng, CH. Hsu, JK. Lin, MM. Hsu, YF. Ho, TS. Shen, JY. Ko, JT. Lin, BR. Lin, Phase I clinical trial of curcumin, a chemopreventive agent, in patients with high-risk or pre-malignant lesions., Anticancer Res, volume 21, issue 4B, pages 2895-900, PMID 11712783
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 B. Chandran, A. Goel, A randomized, pilot study to assess the efficacy and safety of curcumin in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis., Phytother Res, volume 26, issue 11, pages 1719-25, Nov 2012, doi 10.1002/ptr.4639, PMID 22407780
- ↑ S. Ganiger, H.N. Malleshappa, H. Krishnappa, Geetha Rajashekhar, V. Ramakrishna Rao, Frank Sullivan, A two generation reproductive toxicity study with curcumin, turmeric yellow, in Wistar rats, Food and Chemical Toxicology, volume 45, issue 1, 2007, pages 64–69, ISSN 02786915, doi 10.1016/j.fct.2006.07.016
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 V. Kuptniratsaikul, P. Dajpratham, W. Taechaarpornkul, M. Buntragulpoontawee, P. Lukkanapichonchut, C. Chootip, J. Saengsuwan, K. Tantayakom, S. Laongpech, Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts compared with ibuprofen in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a multicenter study., Clin Interv Aging, volume 9, pages 451-8, 2014, doi 10.2147/CIA.S58535, PMID 24672232
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 P. Anand, HB. Nair, B. Sung, AB. Kunnumakkara, VR. Yadav, RR. Tekmal, BB. Aggarwal, Design of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles formulation with enhanced cellular uptake, and increased bioactivity in vitro and superior bioavailability in vivo., Biochem Pharmacol, volume 79, issue 3, pages 330-8, Feb 2010, doi 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.09.003, PMID 19735646
- ↑ Preetha Anand, Ajaikumar B. Kunnumakkara, Robert A. Newman, Bharat B. Aggarwal, Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Promises, Molecular Pharmaceutics, volume 4, issue 6, 2007, pages 807–818, ISSN 1543-8384, doi 10.1021/mp700113r
- ↑ Thierry Appelboom, Nathalie Maes, Adelin Albert, A New Curcuma Extract (Flexofytol®) in Osteoarthritis: Results from a Belgian Real-Life Experience, The Open Rheumatology Journal, volume 8, issue 1, 2014, pages 77–81, ISSN 18743129, doi 10.2174/1874312901408010077
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 F. Drobnic, J. Riera, G. Appendino, S. Togni, F. Franceschi, X. Valle, A. Pons, J. Tur, Reduction of delayed onset muscle soreness by a novel curcumin delivery system (Meriva): a randomised, placebo-controlled trial., J Int Soc Sports Nutr, volume 11, pages 31, 2014, doi 10.1186/1550-2783-11-31, PMID 24982601
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 KA. Agarwal, CD. Tripathi, BB. Agarwal, S. Saluja, Efficacy of turmeric (curcumin) in pain and postoperative fatigue after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled study., Surg Endosc, volume 25, issue 12, pages 3805-10, Dec 2011, doi 10.1007/s00464-011-1793-z, PMID 21671126
- ↑ Y. Panahi, AR. Rahimnia, M. Sharafi, G. Alishiri, A. Saburi, A. Sahebkar, Curcuminoid treatment for knee osteoarthritis: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial., Phytother Res, volume 28, issue 11, pages 1625-31, Nov 2014, doi 10.1002/ptr.5174, PMID 24853120
- ↑ V. Kuptniratsaikul, S. Thanakhumtorn, P. Chinswangwatanakul, L. Wattanamongkonsil, V. Thamlikitkul, Efficacy and safety of Curcuma domestica extracts in patients with knee osteoarthritis., J Altern Complement Med, volume 15, issue 8, pages 891-7, Aug 2009, doi 10.1089/acm.2008.0186, PMID 19678780
- ↑ X. Zhu, Q. Li, R. Chang, D. Yang, Z. Song, Q. Guo, C. Huang, Curcumin alleviates neuropathic pain by inhibiting p300/CBP histone acetyltransferase activity-regulated expression of BDNF and cox-2 in a rat model., PLoS One, volume 9, issue 3, pages e91303, 2014, doi 10.1371/journal.pone.0091303, PMID 24603592
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 LM. Nicol, DS. Rowlands, R. Fazakerly, J. Kellett, Curcumin supplementation likely attenuates delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS)., Eur J Appl Physiol, volume 115, issue 8, pages 1769-77, Aug 2015, doi 10.1007/s00421-015-3152-6, PMID 25795285
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Brian K. McFarlin, Adam S. Venable, Andrea L. Henning, Jill N. Best Sampson, Kathryn Pennel, Jakob L. Vingren, David W. Hill, Reduced Inflammatory and Muscle Damage Biomarkers following Oral Supplementation with Bioavailable Curcumin, BBA Clinical, 2016, ISSN 22146474, doi 10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.02.003
- ↑ 34.0 34.1 34.2 Yoko Tanabe, Seiji Maeda, Nobuhiko Akazawa, Asako Zempo-Miyaki, Youngju Choi, Song-Gyu Ra, Atsushi Imaizumi, Yoshihiko Otsuka, Kazunori Nosaka, Attenuation of indirect markers of eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage by curcumin, European Journal of Applied Physiology, volume 115, issue 9, 2015, pages 1949–1957, ISSN 1439-6319, doi 10.1007/s00421-015-3170-4
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 JM. Davis, EA. Murphy, MD. Carmichael, MR. Zielinski, CM. Groschwitz, AS. Brown, JD. Gangemi, A. Ghaffar, EP. Mayer, Curcumin effects on inflammation and performance recovery following eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage., Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, volume 292, issue 6, pages R2168-73, Jun 2007, doi 10.1152/ajpregu.00858.2006, PMID 17332159
- ↑ N. Kawanishi, K. Kato, M. Takahashi, T. Mizokami, Y. Otsuka, A. Imaizumi, D. Shiva, H. Yano, K. Suzuki, Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress following downhill running-induced muscle damage., Biochem Biophys Res Commun, volume 441, issue 3, pages 573-8, Nov 2013, doi 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.10.119, PMID 24184481
- ↑ Y. Henrotin, M. Gharbi, Y. Dierckxsens, F. Priem, M. Marty, L. Seidel, A. Albert, E. Heuse, V. Bonnet, Decrease of a specific biomarker of collagen degradation in osteoarthritis, Coll2-1, by treatment with highly bioavailable curcumin during an exploratory clinical trial., BMC Complement Altern Med, volume 14, pages 159, 2014, doi 10.1186/1472-6882-14-159, PMID 24886572
- ↑ A. Bertolini, A. Ottani, M. Sandrini, Selective COX-2 inhibitors and dual acting anti-inflammatory drugs: critical remarks., Curr Med Chem, volume 9, issue 10, pages 1033-43, May 2002, PMID 12733982
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 CJ. Hawkey, COX-1 and COX-2 inhibitors., Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol, volume 15, issue 5, pages 801-20, Oct 2001, doi 10.1053/bega.2001.0236, PMID 11566042
- ↑ N. Futaki, S. Takahashi, M. Yokoyama, I. Arai, S. Higuchi, S. Otomo, NS-398, a new anti-inflammatory agent, selectively inhibits prostaglandin G/H synthase/cyclooxygenase (COX-2) activity in vitro, Prostaglandins, volume 47, issue 1, 1994, pages 55–59, ISSN 00906980, doi 10.1016/0090-6980(94)90074-4
- ↑ CJ Hawkey, COX-2 inhibitors, The Lancet, volume 353, issue 9149, 1999, pages 307–314, ISSN 01406736, doi 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)12154-2
- ↑ T. Moini Zanjani, H. Ameli, F. Labibi, K. Sedaghat, M. Sabetkasaei, The Attenuation of Pain Behavior and Serum COX-2 Concentration by Curcumin in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain., Korean J Pain, volume 27, issue 3, pages 246-52, Jul 2014, doi 10.3344/kjp.2014.27.3.246, PMID 25031810
- ↑ K. Moriyuki, F. Sekiguchi, K. Matsubara, H. Nishikawa, A. Kawabata, Curcumin Inhibits the proteinase-activated receptor-2-triggered prostaglandin E2 production by suppressing cyclooxygenase-2 upregulation and Akt-dependent activation of nuclear factor-κB in human lung epithelial cells., J Pharmacol Sci, volume 114, issue 2, pages 225-9, 2010, PMID 20838026
- ↑ C. Ireson, S. Orr, DJ. Jones, R. Verschoyle, CK. Lim, JL. Luo, L. Howells, S. Plummer, R. Jukes, Characterization of metabolites of the chemopreventive agent curcumin in human and rat hepatocytes and in the rat in vivo, and evaluation of their ability to inhibit phorbol ester-induced prostaglandin E2 production., Cancer Res, volume 61, issue 3, pages 1058-64, Feb 2001, PMID 11221833
- ↑ S. Lev-Ari, A. Starr, A. Vexler, V. Karaush, V. Loew, J. Greif, E. Fenig, D. Aderka, R. Ben-Yosef, Inhibition of pancreatic and lung adenocarcinoma cell survival by curcumin is associated with increased apoptosis, down-regulation of COX-2 and EGFR and inhibition of Erk1/2 activity., Anticancer Res, volume 26, issue 6B, pages 4423-30, PMID 17201164
- ↑ SM. Plummer, KA. Holloway, MM. Manson, RJ. Munks, A. Kaptein, S. Farrow, L. Howells, Inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-kappaB activation via the NIK/IKK signalling complex., Oncogene, volume 18, issue 44, pages 6013-20, Oct 1999, doi 10.1038/sj.onc.1202980, PMID 10557090
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 47.2 R.S. Ramsewak, D.L. DeWitt, M.G. Nair, Cytotoxicity, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Curcumins I–III from Curcuma longa, Phytomedicine, volume 7, issue 4, 2000, pages 303–308, ISSN 09447113, doi 10.1016/S0944-7113(00)80048-3
- ↑ Y. Henrotin, AL. Clutterbuck, D. Allaway, EM. Lodwig, P. Harris, M. Mathy-Hartert, M. Shakibaei, A. Mobasheri, Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes., Osteoarthritis Cartilage, volume 18, issue 2, pages 141-9, Feb 2010, doi 10.1016/j.joca.2009.10.002, PMID 19836480
- ↑ Exertional rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure... [Sports Med. 2007] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17465608
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 http://journals.lww.com/acsm-csmr/Abstract/2010/03000/Athletes,_NSAID,_Coxibs,_and_the_Gastrointestinal.11.aspx
- ↑ KIDNEY FAILURE AND ULTRAMARATHONING http://www.lehigh.edu/\~dmd1/kidney.html
- ↑ Recurrent rhabdomyolysis in a collegiat... [Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16540825
- ↑ NSAID Use Increases the Risk of Developing Hyponatremia duri... : Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise http://journals.lww.com/acsm-msse/Abstract/2006/04000/NSAID_Use_Increases_the_Risk_of_Developing.2.aspx
- ↑ http://journals.lww.com/cjsportsmed/Abstract/2007/01000/Exercise_Associated_Hyponatremia,_Renal_Function,.8.aspx
- ↑ http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0002934307001672
- ↑ http://journals.lww.com/cjsportsmed/Abstract/2003/01000/The_Incidence,_Risk_Factors,_and_Clinical.8.aspx
- ↑ CL. Dumke, DC. Nieman, K. Oley, RH. Lind, Ibuprofen does not affect serum electrolyte concentrations after an ultradistance run., Br J Sports Med, volume 41, issue 8, pages 492-6; discussion 496, Aug 2007, doi 10.1136/bjsm.2006.033597, PMID 17331976
- ↑ FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA strengthens warning that non-aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can cause heart attacks or strokes, http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm451800.htm, Accessed on 25 January 2016
- ↑ K. Cheung, P. Hume, L. Maxwell, Delayed onset muscle soreness : treatment strategies and performance factors., Sports Med, volume 33, issue 2, pages 145-64, 2003, PMID 12617692
- ↑ Smith LL. Causes of delayed onset muscle soreness and the impact on athletic performance: a review. J Appl Sport Sci Res 1992; 6 (3): 135-41
- ↑ A. Baldwin Lanier, Use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs following exercise-induced muscle injury., Sports Med, volume 33, issue 3, pages 177-85, 2003, PMID 12656639
- ↑ G. Howatson, KA. van Someren, The prevention and treatment of exercise-induced muscle damage., Sports Med, volume 38, issue 6, pages 483-503, 2008, PMID 18489195
- ↑ DK. Mishra, J. Fridén, MC. Schmitz, RL. Lieber, Anti-inflammatory medication after muscle injury. A treatment resulting in short-term improvement but subsequent loss of muscle function., J Bone Joint Surg Am, volume 77, issue 10, pages 1510-9, Oct 1995, PMID 7593059
- ↑ 64.0 64.1 SM. Hasson, JC. Daniels, JG. Divine, BR. Niebuhr, S. Richmond, PG. Stein, JH. Williams, Effect of ibuprofen use on muscle soreness, damage, and performance: a preliminary investigation., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 25, issue 1, pages 9-17, Jan 1993, PMID 8423760
- ↑ 65.0 65.1 Tokmakidis SP, Kokkinidis EA, Smilios I, Douda H, The effects of ibuprofen on delayed muscle soreness and muscular performance after eccentric exercise., J Strength Cond Res, 2003, volume 17, issue 1, pages 53-9, PMID 12580656
- ↑ 66.0 66.1 Effect of Ibuprofen Use on Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness of the Elbow Flexors http://journals.humankinetics.com/jsr-back-issues/jsrvolume4issue4november/effectofibuprofenuseondelayedonsetmusclesorenessoftheelbowflexors
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 FX. Pizza, D. Cavender, A. Stockard, H. Baylies, A. Beighle, Anti-inflammatory doses of ibuprofen: effect on neutrophils and exercise-induced muscle injury., Int J Sports Med, volume 20, issue 2, pages 98-102, Feb 1999, doi 10.1055/s-2007-971100, PMID 10190769
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 N Rahnama, F Rahmani-Nia, K Ebrahim, The isolated and combined effects of selected physical activity and ibuprofen on delayed-onset muscle soreness, Journal of Sports Sciences, volume 23, issue 8, 2005, pages 843–850, ISSN 0264-0414, doi 10.1080/02640410400021989
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 Joel R. Krentz, Braden Quest, Jonathan P. Farthing, Dale W. Quest, Philip D. Chilibeck, The effects of ibuprofen on muscle hypertrophy, strength, and soreness during resistance training, Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, volume 33, issue 3, 2008, pages 470–475, ISSN 1715-5312, doi 10.1139/H08-019
- ↑ 70.0 70.1 Lars Arendt-Nielsen, Morten Weidner, Dorte Bartholin, Allan Rosetzsky, A Double-Blind Randomized Placebo Controlled Parallel Group Study Evaluating the Effects of Ibuprofen and Glucosamine Sulfate on Exercise Induced Muscle Soreness, Journal Of Musculoskeletal Pain, volume 15, issue 1, 2007, pages 21–28, ISSN 1058-2452, doi 10.1300/J094v15n01_04
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 AE. Donnelly, RJ. Maughan, PH. Whiting, Effects of ibuprofen on exercise-induced muscle soreness and indices of muscle damage., Br J Sports Med, volume 24, issue 3, pages 191-5, Sep 1990, PMID 2078806
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 72.2 MB. Stone, MA. Merrick, CD. Ingersoll, JE. Edwards, Preliminary comparison of bromelain and Ibuprofen for delayed onset muscle soreness management., Clin J Sport Med, volume 12, issue 6, pages 373-8, Nov 2002, PMID 12466693
- ↑ Robert D. Hyldahl, Justin Keadle, Pierre A. Rouzier, Dennis Pearl, Priscilla M. Clarkson, Effects of Ibuprofen Topical Gel on Muscle Soreness, Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, volume 42, issue 3, 2010, pages 614–621, ISSN 0195-9131, doi 10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181b95db2
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 74.2 P. Barlas, JA. Craig, J. Robinson, DM. Walsh, GD. Baxter, JM. Allen, Managing delayed-onset muscle soreness: lack of effect of selected oral systemic analgesics., Arch Phys Med Rehabil, volume 81, issue 7, pages 966-72, Jul 2000, doi 10.1053/apmr.2000.6277, PMID 10896014
- ↑ 75.0 75.1 Lucille Smith, Robert George, Thomas Chenier, Michael McCammon, Joseph Houmard, Richard Israel, R. A. Hoppmann, Susan Smith, Do over-the-counter analgesics reduce delayed onset muscle soreness and serum creatine kinase values?, Research in Sports Medicine, volume 6, issue 2, 1995, pages 81–88, ISSN 1543-8627, doi 10.1080/15438629509512039
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 Riasati et al.: Aspirin and delayed onset muscle soreness ASPIRIN MAY BE AN EFFECTIVE TREATMENT FOR EXERCISE- INDUCED MUSCLE SORENESS | ResearchGate http://www.researchgate.net/publication/228091056_Riasati_et_al._Aspirin_and_delayed_onset_muscle_soreness_ASPIRIN_MAY_BE_AN_EFFECTIVE_TREATMENT_FOR_EXERCISE-_INDUCED_MUSCLE_SORENESS
- ↑ 77.0 77.1 KT. Francis, T. Hoobler, Effects of aspirin on delayed muscle soreness., J Sports Med Phys Fitness, volume 27, issue 3, pages 333-7, Sep 1987, PMID 3431117
- ↑ 78.0 78.1 GA. Dudley, J. Czerkawski, A. Meinrod, G. Gillis, A. Baldwin, M. Scarpone, Efficacy of naproxen sodium for exercise-induced dysfunction muscle injury and soreness., Clin J Sport Med, volume 7, issue 1, pages 3-10, Jan 1997, PMID 9117523
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 AC. Baldwin, SW. Stevenson, GA. Dudley, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory therapy after eccentric exercise in healthy older individuals., J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, volume 56, issue 8, pages M510-3, Aug 2001, PMID 11487604
- ↑ 80.0 80.1 JM. Lecomte, VJ. Lacroix, DL. Montgomery, A randomized controlled trial of the effect of naproxen on delayed onset muscle soreness and muscle strength., Clin J Sport Med, volume 8, issue 2, pages 82-7, Apr 1998, PMID 9641434
- ↑ The Effect of Taking Naproxen Drug on the Level of Perceived Pain and Changes of CPK Serum after Eccentric Exercise - Harakat Volume: 37, Issue:, Accessed on 3 January 2013
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 J. Bourgeois, D. MacDougall, J. MacDonald, M. Tarnopolsky, Naproxen does not alter indices of muscle damage in resistance-exercise trained men., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 31, issue 1, pages 4-9, Jan 1999, PMID 9927002
- ↑ A E Donnelly, K McCormick, R J Maughan, P H Whiting, P M Clarkson, Effects of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug on delayed onset muscle soreness and indices of damage., British Journal of Sports Medicine, volume 22, issue 1, 1988, pages 35–38, ISSN 0306-3674, doi 10.1136/bjsm.22.1.35
- ↑ L.C. Loram, D. Mitchell, A. Fuller, Rofecoxib and tramadol do not attenuate delayed-onset muscle soreness or ischaemic pain in human volunteers, Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, volume 83, issue 12, 2005, pages 1137–1145, ISSN 0008-4212, doi 10.1139/y05-113
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 SP. Sayers, CA. Knight, PM. Clarkson, EH. Van Wegen, G. Kamen, Effect of ketoprofen on muscle function and sEMG activity after eccentric exercise., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 33, issue 5, pages 702-10, May 2001, PMID 11323536
- ↑ K. van Wijck, K. Lenaerts, LJ. van Loon, WH. Peters, WA. Buurman, CH. Dejong, Exercise-induced splanchnic hypoperfusion results in gut dysfunction in healthy men., PLoS One, volume 6, issue 7, pages e22366, 2011, doi 10.1371/journal.pone.0022366, PMID 21811592
- ↑ K. VAN Wijck, K. Lenaerts, AA. VAN Bijnen, B. Boonen, LJ. VAN Loon, CH. Dejong, WA. Buurman, Aggravation of exercise-induced intestinal injury by Ibuprofen in athletes., Med Sci Sports Exerc, volume 44, issue 12, pages 2257-62, Dec 2012, doi 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318265dd3d, PMID 22776871
- ↑ IC. Vermeulen Windsant, FA. Hellenthal, JP. Derikx, MH. Prins, WA. Buurman, MJ. Jacobs, GW. Schurink, Circulating intestinal fatty acid-binding protein as an early marker of intestinal necrosis after aortic surgery: a prospective observational cohort study., Ann Surg, volume 255, issue 4, pages 796-803, Apr 2012, doi 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31824b1e16, PMID 22367448
- ↑ Wayne K. Stadelmann, Alexander G. Digenis, Gordon R. Tobin, Impediments to wound healing, The American Journal of Surgery, volume 176, issue 2, 1998, pages 39S–47S, ISSN 00029610, doi 10.1016/S0002-9610(98)00184-6
- ↑ S. Guo, L. A. DiPietro, Factors Affecting Wound Healing, Journal of Dental Research, volume 89, issue 3, 2010, pages 219–229, ISSN 0022-0345, doi 10.1177/0022034509359125
- ↑ Ibuprofen use during extreme exercise: ... [Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17596774
- ↑ Ibuprofen use, endotoxemia, inflammation, ... [Brain Behav Immun. 2006] - PubMed - NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16554145
- ↑ Ibuprofen Official FDA information, side effects and uses. http://www.drugs.com/pro/ibuprofen.html
- ↑ Ibuprofen/Famotidine Reduces Gastric Ulcer Incidence http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/732432
- ↑ Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: Results of a United States multicenter, prospective study - Larson - 2005 - Hepatology - Wiley Online Library http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hep.20948/pdf
- ↑ 96.0 96.1 96.2 96.3 Staggered overdose pattern and delay to hospital presentation are associated with adverse outcomes following paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04067.x/full
- ↑ FDA May Restrict Acetaminophen http://www.webmd.com/pain-management/news/20090701/fda-may-restrict-acetaminophen
- ↑ ACETAMINOPHEN (PARACETAMOL) http://www.chemicalland21.com/lifescience/phar/ACETAMINOPHEN.htm
- ↑ GG. Graham, KF. Scott, Mechanism of action of paracetamol., Am J Ther, volume 12, issue 1, pages 46-55, PMID 15662292
- ↑ Regina Botting, Samir S. Ayoub, COX-3 and the mechanism of action of paracetamol/acetaminophen, Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids, volume 72, issue 2, 2005, pages 85–87, ISSN 09523278, doi 10.1016/j.plefa.2004.10.005
- ↑ K. Toussaint, X. C. Yang, M. A. Zielinski, K. L. Reigle, S. D. Sacavage, S. Nagar, R. B. Raffa, What do we (not) know about how paracetamol (acetaminophen) works?, Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, volume 35, issue 6, 2010, pages 617–638, ISSN 02694727, doi 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01143.x
- ↑ Brian J. Anderson, Paracetamol (Acetaminophen): mechanisms of action, Pediatric Anesthesia, volume 18, issue 10, 2008, pages 915–921, ISSN 11555645, doi 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2008.02764.x
- Category:Training
- Category:Injury
- Category:Science